Schedule 3 Balance Sheet Format
Vyapar automates Schedule 3 balance sheets flawlessly, ensuring accuracy, saving time, and offering insights in seconds. Download Vyapar now to streamline your financial reporting and improve your business efficiency.
⚡️ Eliminate errors with pre-defined formulas
⚡ Simplify calculations and save time
⚡️ Generate accurate balance sheets in minutes

Download Free Schedule 3 Balance Sheet Format
Download free Schedule 3 Balance Sheet Format in Excel, Word, Pdf, and make customization according to your requirements at zero cost.


Customize Invoices
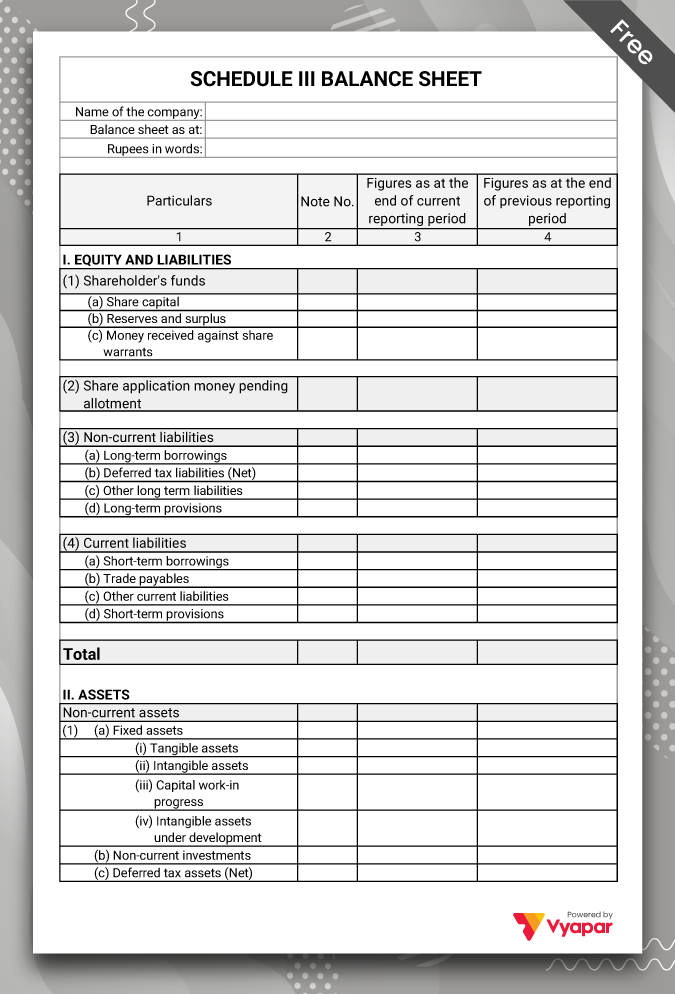
Schedule 3 Balance Sheet Format Type I

Schedule 3 Balance Sheet Format Type II
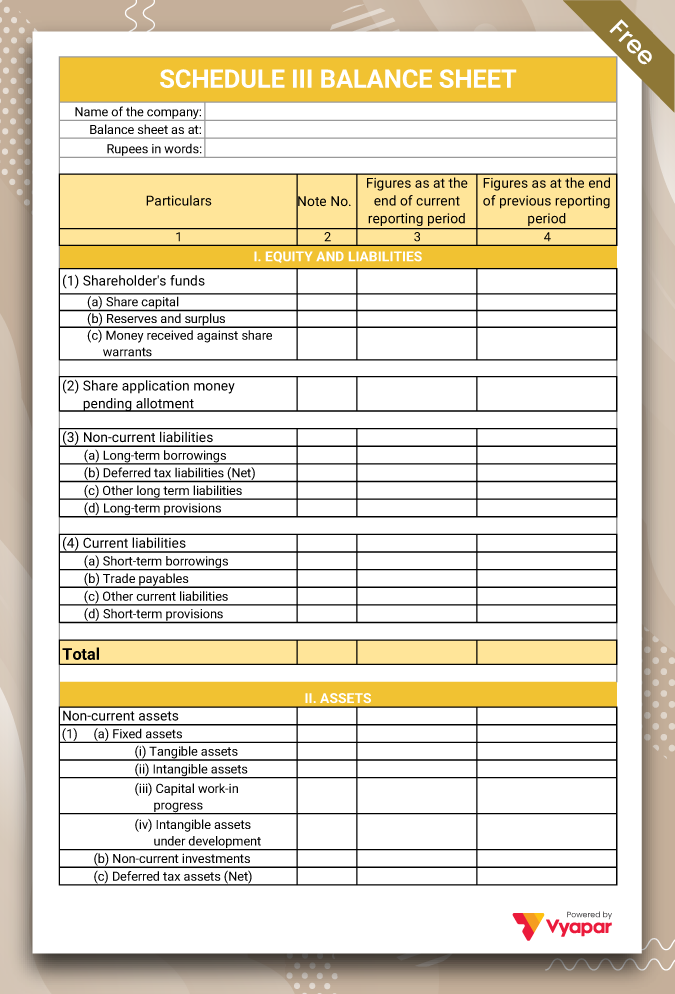
Schedule 3 Balance Sheet Format Type III

Schedule 3 Balance Sheet Format Type IV
Generate Invoice Online
Get 50+ Customized Schedule III Balance Sheet Templates. Try it Vyapar for FREE!
Highlights of Schedule III Balance Sheet Simple Templates
We’ve put in a lot of effort to make sure you get the best template possible

All versions are print friendly

Built From scratch

Include essential invoice elements

Automatically calculate subtotal and grand total amounts

Consistently formatted
What is Schedule 3 of the Balance Sheet?
The Schedule 3 balance sheet is similar to a regular balance sheet. It includes the financial information of all company subsidiaries. This creates a consolidated balance sheet. The balance sheet is typically included in a company’s annual report. It gives a detailed overview of the company’s assets, liabilities, and overall value as of a specific date. The balance sheet shows what the company owns and what it owes. It provides a snapshot of the company’s financial health at a given point in time. A provisional balance sheet is a preliminary statement that can change. A vertical balance sheet lists assets, liabilities, and equity in a vertical layout.
On October 11, 2018, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) amended Schedule III of the Companies Act 2013. Companies must format their financial statements according to Accounting Standards (AS) and Ind AS in Division I and Division II. This change outlines the required formatting for financial statements. The formatting must adhere to the guidelines set by AS and Ind AS. Division I and Division II have specific requirements for financial statement formatting, Now, Schedule III is also applicable to NBFCs covered under Ind AS, ensuring standardized reporting across various sectors.
Schedule III Divided into three Parts

Division I: Financial Statements for a company that must comply with the Companies (Accounting Standards) Rules, 2006.
Division II: Financial Statements for a company that adheres to the Companies (Indian Accounting Standards) Rules, 2015.Division III: Financial Statements for a Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) that follows the Companies (Indian Accounting Standards) Rules, 2015.
Key Features of the Vyapar Schedule III Balance Sheet Maker App
Accounting Security:
The best cloud-based accounting features in the Vyapar schedule 3 balance sheet generator ensure that your records remain securely stored. Your data is fully constantly synced and safeguarded with high-end encryption algorithms.
Vyapar App prioritizes user privacy, never storing Google data, and always displaying any collected data to the user. For added security, changing passwords regularly and keeping backups offline is recommended.


Simplified Tax Compliance:
The free schedule 3 balance sheet maker app simplifies tax compliance by maintaining accurate accounting records and up-to-date financial statements.
With advanced online accounting software by Vyapar, tax rules are integrated, freeing you to focus on business growth instead of IRS concerns. Gathering documents and information required for tax filing becomes straightforward with this feature.
Business Reports:
After creating invoices, leverage the collected data to quickly generate balance sheets and sales or purchase reports. These reports offer insights into various growth metrics of your business.
Easily create inventory reports to identify product demand and ensure adequate stock levels. Seamlessly file taxes and GST with the assistance of tax statements.

Manage all transactions:
The free Balance Sheet Format maker empowers you to create and share invoices via multiple channels like WhatsApp and email. It allows for discounts during payments and provides a PIN for transaction deletion.
Sellers can add extra charges such as shipping or packaging to invoices and assess profits while creating new sale invoices.
Bank Accounts:
Efficiently manage payments by easily adding, managing, and tracking them using Vyapar’s accounting and billing software.
With support for multiple payment modes, you can swiftly enter revenue data from banks or e-wallets. Ensure proper account management by integrating your bank with Vyapar software and access data from anywhere with internet connectivity.

Inventory Control:
Streamline inventory management with the Vyapar accounting balance sheet maker, ensuring you track the items needed for selling services or products.
Avoid operational disruptions due to inventory shortages and identify surplus inventory to prevent unnecessary purchases. This feature empowers your businesses to maintain optimal inventory levels for smooth operations.
Access Data Any Time, Anywhere:
One of the key advantages of cloud accounting software is the ability to access your data anytime, from any device.
Whether you can use a desktop or mobile phone, you only need an internet connection. This flexibility lets you create and send invoices directly from your mobile device.


Save Time With Automation:
Manual bookkeeping tasks like creating invoices, tracking transactions, and logging journal entries can be time-consuming.
Accounting Software Vyapar automates these processes, linking your accounts for automatic journal entries and invoice creation easily. You can also set up automatic payment reminders and send them to your debtors.
Ensure Accounting Accuracy:
The Vyapar App guarantees accurate and adequate accounting records. The Schedule 3 balance sheet format minimizes human error during data entry and computation. You will be alerted by the system in case of an error while entering data or any mistakes in the data.
It definitely ensures that all documents are readily available at tax filing and reminds you to collect debts and pay dues. The user can rely on the information as it is automated and accurate.


Reduce Paperwork and Improve Sustainability:
With the user-friendly Schedule 3 balance sheet formats in the Vyapar app, you can create copies with a click, eliminating the need for manual photocopying.
Invoices and records are stored with cloud encryption, accessible only with the correct permissions. You can also send invoices directly from the software, saving time and money on printing and posting.
So What are you waiting for?
Take your business to the next level with Vyapar! Try free for 7 days
Try our Android App (FREE for lifetime)
Using Schedule 3 Balance Sheets for Enhanced Business Operations
The Schedule 3 balance sheets provide a detailed overview of a company’s financial position, including information on assets, liabilities & equity. By leveraging these balance sheets, businesses can:
- Evaluate Financial Well-being: Schedule 3 balance sheet offers a thorough analysis, empowering businesses to assess their financial health with precision.
- Facilitate Strategic Decision-Making: With clear visibility into assets, liabilities, and equity, companies can make informed decisions to drive growth and profitability.
- Ensure Compliance: Adhering to regulatory requirements is crucial for any business. Schedule 3 balance sheets aid in meeting compliance standards & fostering trust among stakeholders.
- Streamline Reporting: These balance sheets simplify the reporting process, allowing businesses to present financial information in a structured format.
Integrating Schedule 3 balance sheets into financial management practices can enhance your business transparency, efficiency & sustainability across all scales.
Components of a Schedule 3 Balance Sheet
The Schedule 3 balance sheet provides a comprehensive view of a company’s financial position by detailing various components:
Assets:
Current assets: Cash, inventory, accounts receivable, etc.
Non-current assets: Property, plant, equipment, intangible assets, etc.
Liabilities:
Current Liabilities: Accounts payable, short-term loans, etc.
Non-current liabilities: Long-term debt, deferred tax liabilities, etc.
Equity:
Stockholder’s equity: Common stock, retained earnings, additional paid-in capital, etc.
Minority interest: Equity interests in wholly owned subsidiaries of a company.
Understanding all these components is essential to assessing the financial health and stability of your business, as the Schedule 3 balance sheet format includes the financial data of all company subsidiaries.
Importance of a Schedule 3 Balance Sheet

The Schedule 3 balance sheet format is important to businesses and stakeholders because:
Comprehensive view: It presents a detailed overview of a company’s financial position, including its assets, liabilities and equity, providing a holistic view of its financial health.
Transparency and Compliance: Ensures transparency and compliance with regulatory standards such as the Companies Act 2013 by providing a structured format for financial reporting.
Decision making tool: It helps stakeholders including investors and management to take informed decisions by analyzing the financial performance and stability of the company.
In short, the Schedule 3 balance sheet format serves as a useful & valuable tool to assess financial health, ensure compliance, and facilitate strategic decision-making for every business.
Limitations of a Schedule 3 Balance Sheet
Limited Insight:
While providing a detailed description of a company’s financial position, the Schedule 3 balance sheet may not include all aspects of its operations, such as qualitative factors or future performance indicators.
Lack of timeliness:
Schedule 3 balance sheets are generally prepared for specific reporting periods and may not reflect real-time financial information, limiting their usefulness for decision making.
Complexity:
Due to the inclusion of supporting financial data and adherence to specific accounting standards, interpreting the Schedule 3 balance sheet can be complex and challenging for non-accounting professionals.
Reliance on historical data:
Schedule 3 balance sheets focus primarily on historical financial information and may not adequately reflect current market conditions or emerging trends, limiting their relevance to strategic planning.
Regulatory constraints:
The format and content of the Schedule 3 balance sheet is subject to regulatory requirements, which may restrict flexibility in presentation and reporting, potentially ignoring certain financial aspects.
General Instructions For Preparation of Schedule III Balance Sheet

Changes required for compliance with the Act, including additions, modifications, substitutions, or deletions to financial statement headings or subheads, must be implemented. This Schedule will be adjusted accordingly.
Disclosure requirements outlined in this Schedule III balance sheet are supplementary to those prescribed in Accounting Standards under the Companies Act, 2013. Additional disclosures specified in Accounting Standards must be included in the notes to accounts or supplementary statements, not on the face of the Financial Statements.
Notes to accounts should provide narrative descriptions or disaggregations of recognized items and information about items not qualified for recognition.All entries on the Balance Sheet and Income Statement must correspond to relevant details provided in the accompanying notes to the financial statements.
Financial Statement figures may be rounded off based on turnover. For turnovers less than 100 crore rupees, rounding can be done to hundreds, thousands, lakhs, millions, or decimals. Turnovers exceeding 100 crore rupees can be rounded to lakhs, millions, crores, or decimals.
The first Financial Statements post-incorporation must include comparative amounts for all items, including notes, from the immediately preceding reporting period.
Difference Between Schedule III and Schedule VI Balance Sheet Format
Schedule III of the Companies Act, 2013 provides a format for preparing and presenting financial statements, emphasizing compliance with accounting standards and disclosure requirements. In contrast, the revised Schedule VI under the Companies Act, 1956, adopted the format of financial statements outlined in the Companies Act, 2013, with additional instructions for preparing Consolidated Financial Statements (CFS).
The amended Schedule VI introduces many new concepts & disclosure requirements for the profit and loss statement or balance sheet. In contrast, Schedule III focuses on ensuring compliance with accounting standards & increasing business transparency through detailed disclosure.
Difference Between Comprehensive Balance Sheet and Schedule III Balance Sheet Format
A comprehensive balance sheets provides a flexible overview of a company’s financial position, including or excluding subsidiaries as necessary. It is not bound by specific rules.
However, the Schedule III Balance Sheet follows the strict format required by the Companies Act, 2013. It contains the financial data of all the subsidiaries & ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
Difference Between Balance Sheet and Schedule III Balance Sheet Format
A regular balance sheet shows the assets, liabilities, and equity of a company.
The Schedule III balance sheet follows a specific format required by law & includes detailed disclosures & information about all subsidiaries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs’)
Schedule III of the Companies Act 2013 provides the format of companies’ financial statements complying with Accounting Standards (AS) and Ind AS under its Division I and Division II, respectively.
Schedule III refers to the standardized format for preparing balance sheets as per the Companies Act, 2013, in India. It organizes assets, liabilities, and equity into categories like Shareholder’s Funds, Non-Current Liabilities, Current Liabilities, Non-Current Assets, and Current Assets. This format aims to improve transparency and comparability in financial reporting for companies under the Act.
The Schedule III format for balance sheets underwent significant changes with the Companies Act, 2013. These changes included revised classification of assets, liabilities, and equity, detailed disclosures, standardized financial statement formats, emphasis on notes to accounts, and the requirement for comparative information. These changes aimed to align Indian accounting practices with international standards, enhance transparency, and improve the quality of financial reporting.
The Schedule III format for balance sheets underwent significant changes with the Companies Act, 2013. These changes included revised classification of assets, liabilities, and equity, detailed disclosures, standardized financial statement formats, emphasis on notes to accounts, and the requirement for comparative information.
These changes aimed to align Indian accounting practices with international standards, enhance transparency, and improve the quality of financial reporting.
Yes, Schedule III is applicable to all companies registered under the Companies Act, 2013 in India. It outlines the standardized format for preparing financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, for companies across various industries and sectors.
The objective of Schedule III is to promote uniformity, transparency, and comparability in financial reporting, ensuring that companies present their financial information in a clear, accurate, and consistent manner for stakeholders, investors, regulators, and other interested parties.
The new Schedule III to the Companies Act, 2013, outlines the format for preparing financial statements in India. It includes guidelines for classifying assets, liabilities, and equity, detailed disclosures, comparative information, standardized financial statement formats, and notes to accounts. These changes aim to align Indian accounting standards with international practices, enhance transparency, and improve financial reporting consistency.
Schedule III to the Companies Act, 2013, is typically divided into the following sections:
1. General Instructions: Provides guidelines for preparing financial statements.
2. Balance Sheet Format: Outlines the structure of the balance sheet, including assets, liabilities, and equity.
3. Profit and Loss Statement Format: Specifies the format for the income statement.
4. Cash Flow Statement Format: Provides guidelines for preparing the cash flow statement.
5. Notes to Accounts: Includes additional explanations and disclosures.
6. Accounting Policies: Covers disclosure of accounting policies.





