Balance Sheet Formats in Excel, PDF, Word
Stop struggling with manual balance sheets! Download the free balance sheet format or use the Vyapar app to auto-generate your balance sheet effortlessly.

Balance Sheet Templates Vs Vyapar App
Features
Free Balance Sheet Format

Journal Entry Accounting
Auto Calculation
Expense & Income Tracking
Profit & Loss Reports
Bank & Cash Flow Management
GST Reports
Accounting Integration
Auto Backup
Real-Time Business Insights
Multiple Payment Mode
Free Support and Assistance
Instant Data Sync
Download a Ready-to-Use Free Balance Sheet Format
Thousands of Businesses Trust Vyapar’s Balance Sheet Formats. Download Formats at Zero Cost.
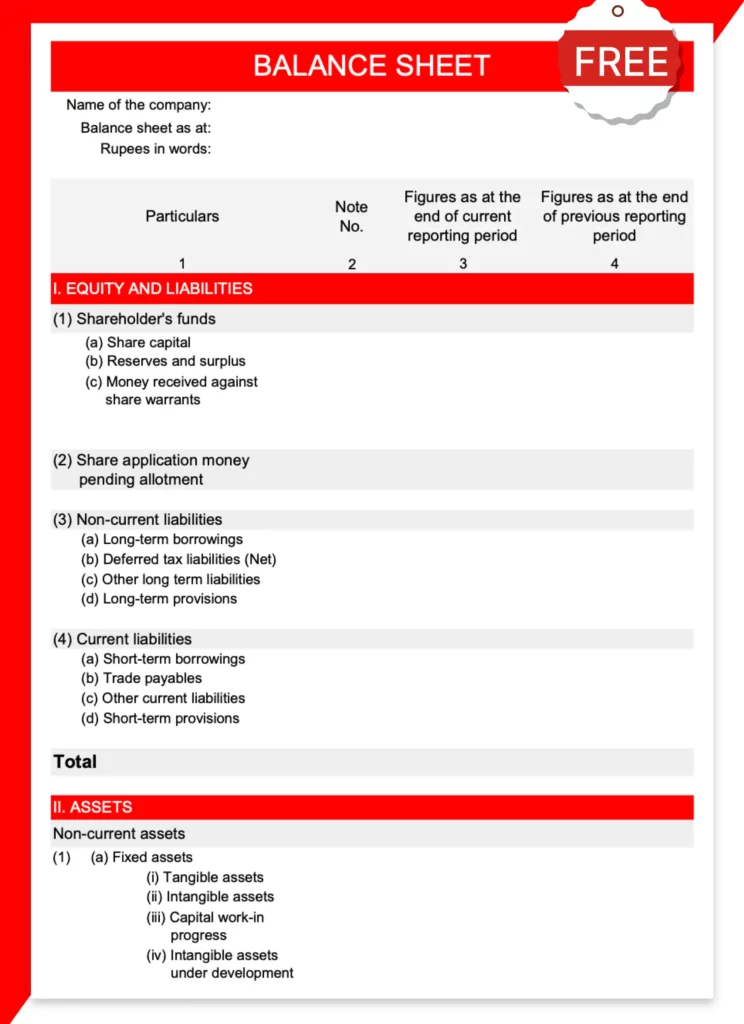
Balance Sheet Template – 01
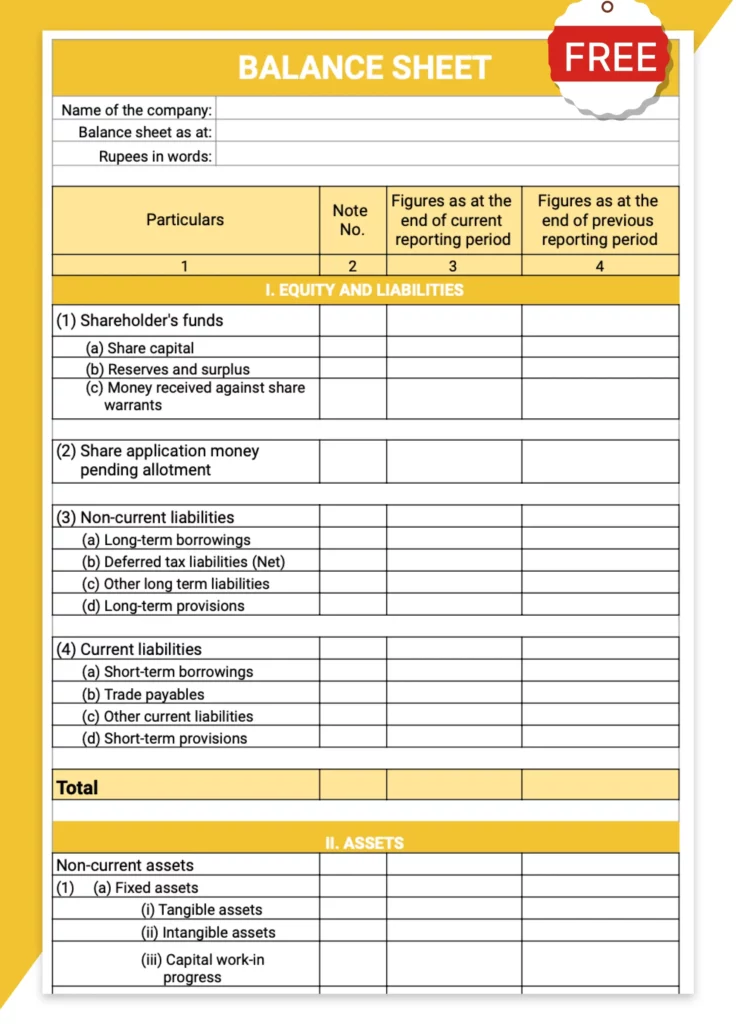
Balance Sheet Template – 02

Balance Sheet Template – 03


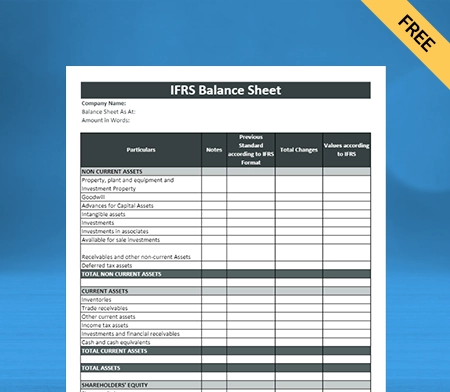
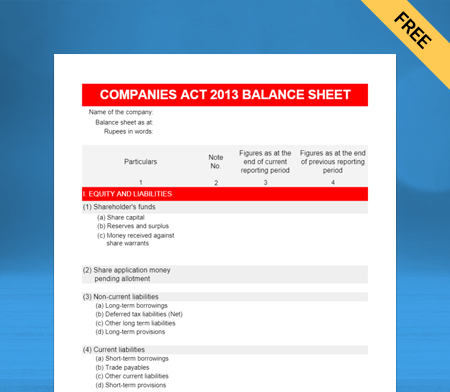
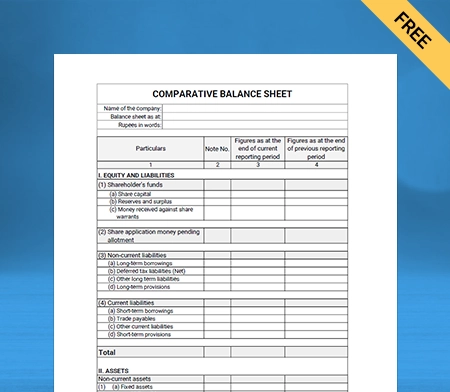


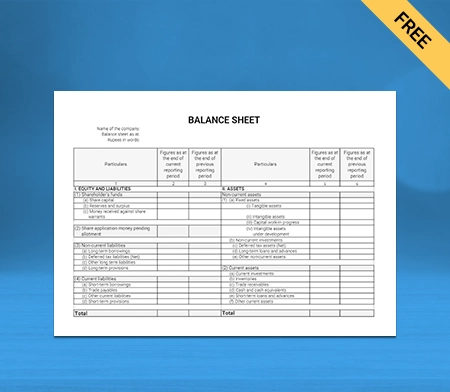
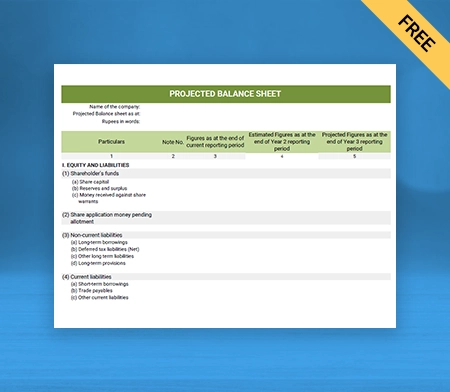

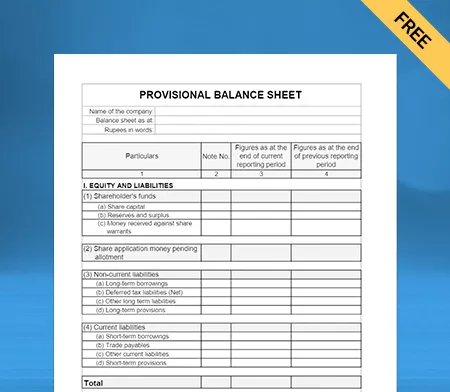
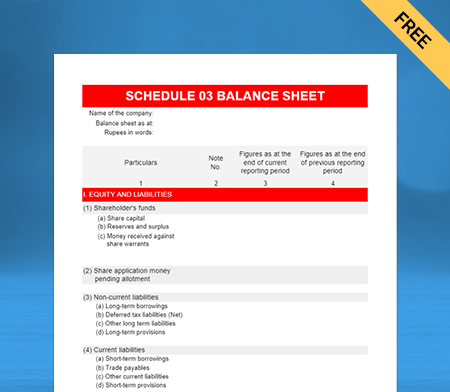
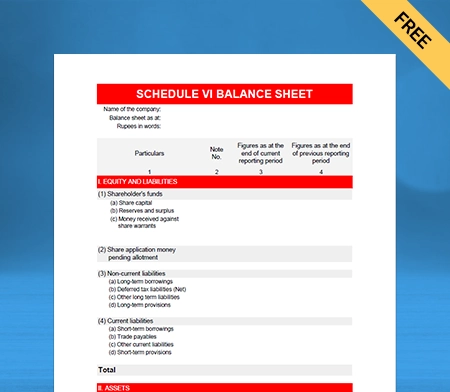


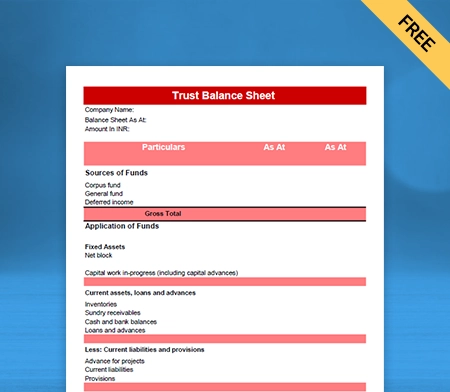
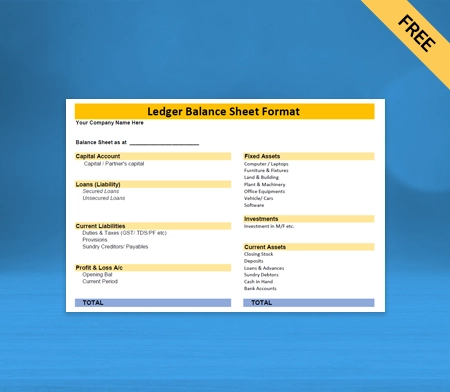
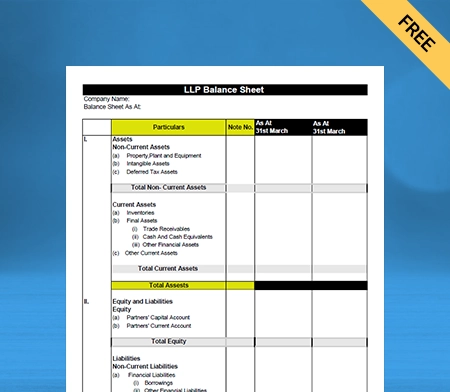
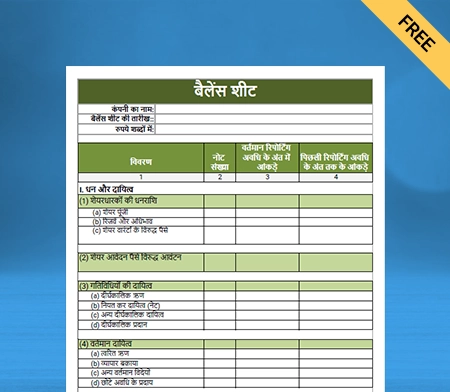
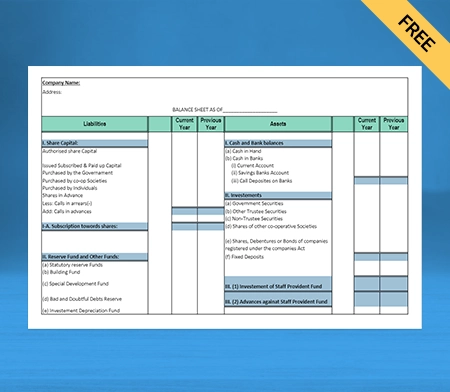
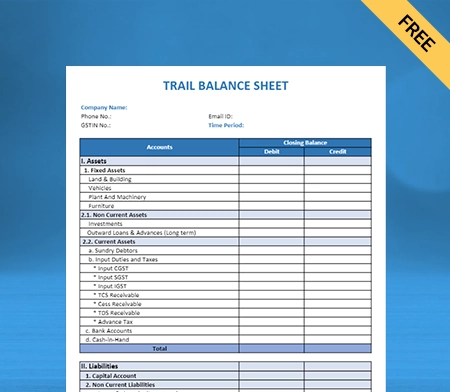

Use Free Balance Sheet Formats to Customize. Try Vyapar for FREE!
What is a Balance Sheet?

A balance sheet is a financial statement that gives an overview of a company’s financial health at a specific point in time. It details the company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity. Assets represent what the company owns, liabilities indicate its financial obligations, and shareholder equity shows the owners’ stake in the business.
🔑 Key Components of a Balance Sheet Format

Title & Business Info
Start with “Balance Sheet” as the title. Add your business name, logo, address, and contact details to give your document a professional identity.

Assets
List all assets the business owns. Current assets include cash, stock, and receivables; non-current assets include property, machines, and long-term investments.

Liabilities
Mention everything your business owes. Current liabilities include bills and taxes due soon; non-current liabilities include loans and lease obligations.

Owner’s Equity
This shows the business’s net worth, including the owner’s capital, retained earnings, and reserves. It reflects your business’s actual value.

Balance Formula
Ensure your sheet follows the rule: Assets = Liabilities + Equity. If not, recheck your entries for mistakes or missing data.

Date & Notes
Mention the exact date of the report and include notes for any special items like policy changes, taxes, or depreciation methods to ensure clarity.
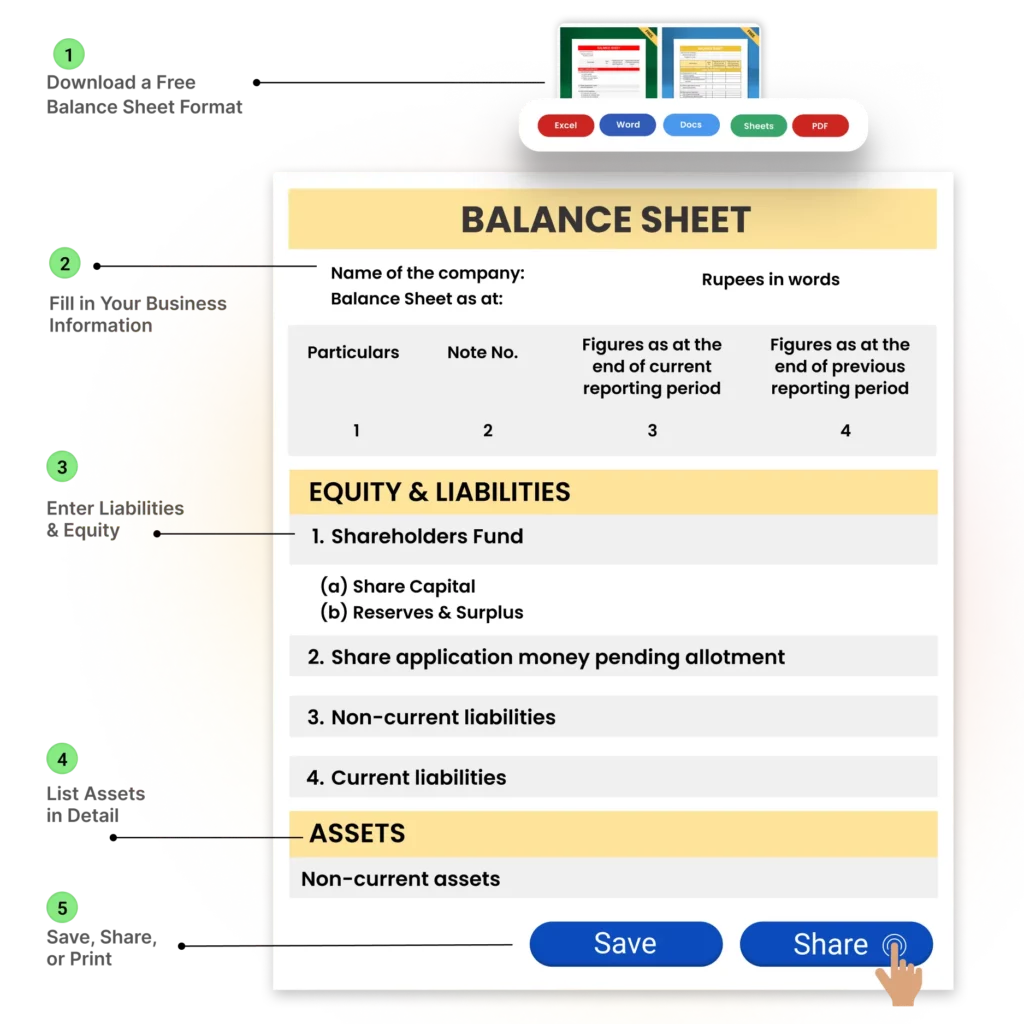
How to Use a Free Balance Sheet Format For Your Business
✅ Step 1: Download a Free Balance Sheet Format: Get a ready-to-use balance sheet template from Vyapar in your preferred format—Excel, Word, or PDF. Choose one that matches your business structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, or company).
✅ Step 2: Fill in Your Business Information: Enter your business name, address, GSTIN (if applicable), and your reporting financial period. This adds professionalism and clarity to the document.
✅ Step 3: List Assets in Detail: Under the “Assets” section, mention current assets like cash, bank balance, receivables, and stock. Then, list non-current assets such as property, vehicles, or long-term investments.
✅ Step 4: Enter Liabilities & Equity: Record your short-term liabilities like loans, creditors, and taxes. Add long-term liabilities like secured loans. Lastly, fill in the owner’s capital, retained earnings, and reserves under the Equity section.
✅ Step 5: Cross-Check the Balance: Make sure the total assets equal the sum of liabilities and equity. Use the balance sheet formula: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity. This step ensures your accounts are accurate.
✅ Step 6: Save, Share, or Print: Once filled, save your balance sheet as a PDF or Excel file. You can print it or share it via email or WhatsApp with your accountant, partners, or stakeholders.
Importance of Balance Sheets
A Balance Sheet is a crucial financial statement that provides a clear picture of a company’s financial position. Here’s why it is essential for businesses:

Evaluates Financial Health
- Shows a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity, helping assess overall stability.
- Helps business owners and investors understand solvency and liquidity.
- Identifies financial strengths and weaknesses for better decision-making.

Aids in Business Decision-Making
- Provides insights into whether the company can expand, invest, or reduce expenses.
- Helps in budgeting and forecasting by analyzing past trends.
- Assists in creditworthiness assessment for loans and investments.

Ensures Compliance & Transparency
- Essential for GST filing and tax compliance.
- Required for audits and legal reporting to maintain financial transparency.
- Helps build trust among stakeholders, investors, and financial institutions.

Assists in Loan & Investment Approvals
- Banks and investors analyze balance sheets before approving loans or investments.
- Shows the company’s ability to repay debts and generate profits.
- Helps in securing better financial opportunities with a strong financial record.

Tracks Business Growth Over Time
- By comparing balance sheets from different periods, businesses can monitor progress.
- Helps track profitability, asset accumulation, and debt reduction.
- Provides a benchmark for setting future financial goals.

Helps in Risk Management
- Identifies high-risk areas such as excessive debt or declining assets.
- Helps business owners take proactive steps to manage risks.
- Ensures better financial planning to handle economic uncertainties.
Why Vyapar is a Better Alternative to the Balance Sheet Format
Vyapar’s customizable formats make tracking assets, liabilities, and net worth easy. Generate daily, monthly, or annual reports, analyze financial projections, and plan for success with our powerful business accounting software.
Integrated Accounting Features
Vyapar App combines invoicing, inventory, and accounting in one seamless platform.
- Auto-sync Transactions: Every sale, purchase, or payment automatically updates your balance sheet—no manual data entry needed.
- Real-Time Ledger Updates: Track your accounts payable/receivable with automatic ledger syncing across transactions.
- GST-Ready Accounting: Vyapar follows Indian tax norms, generating GST-compliant balance sheets and returns effortlessly.

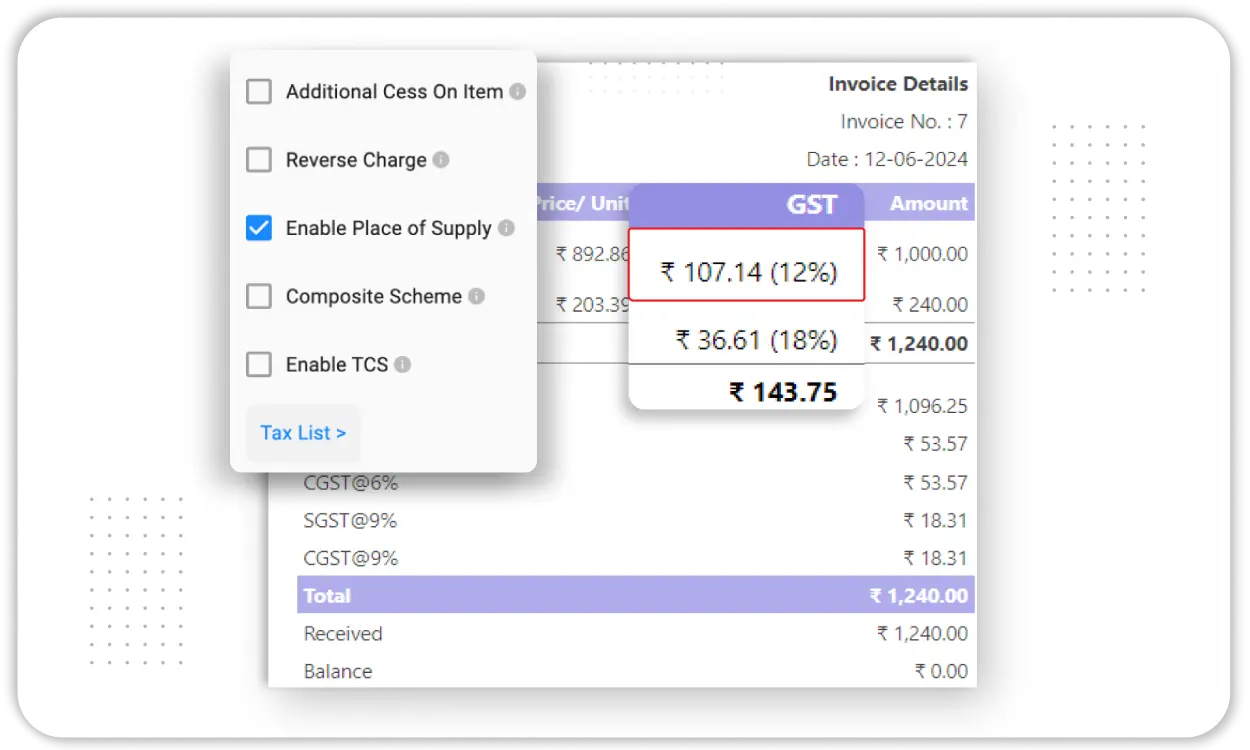
Automation for Accuracy
Manual balance sheets are time-consuming and prone to errors—Vyapar automates key processes.
- Auto-Generated Balance Sheets: Get balance sheets ready in seconds based on real-time data from your transactions.
- Recurring Entries: Schedule recurring expenses or incomes—like rent or subscriptions—with automated ledger entries.
- Auto-Tax Calculations: CGST, SGST, and IGST are auto-applied in reports and reflected in your balance sheet instantly.
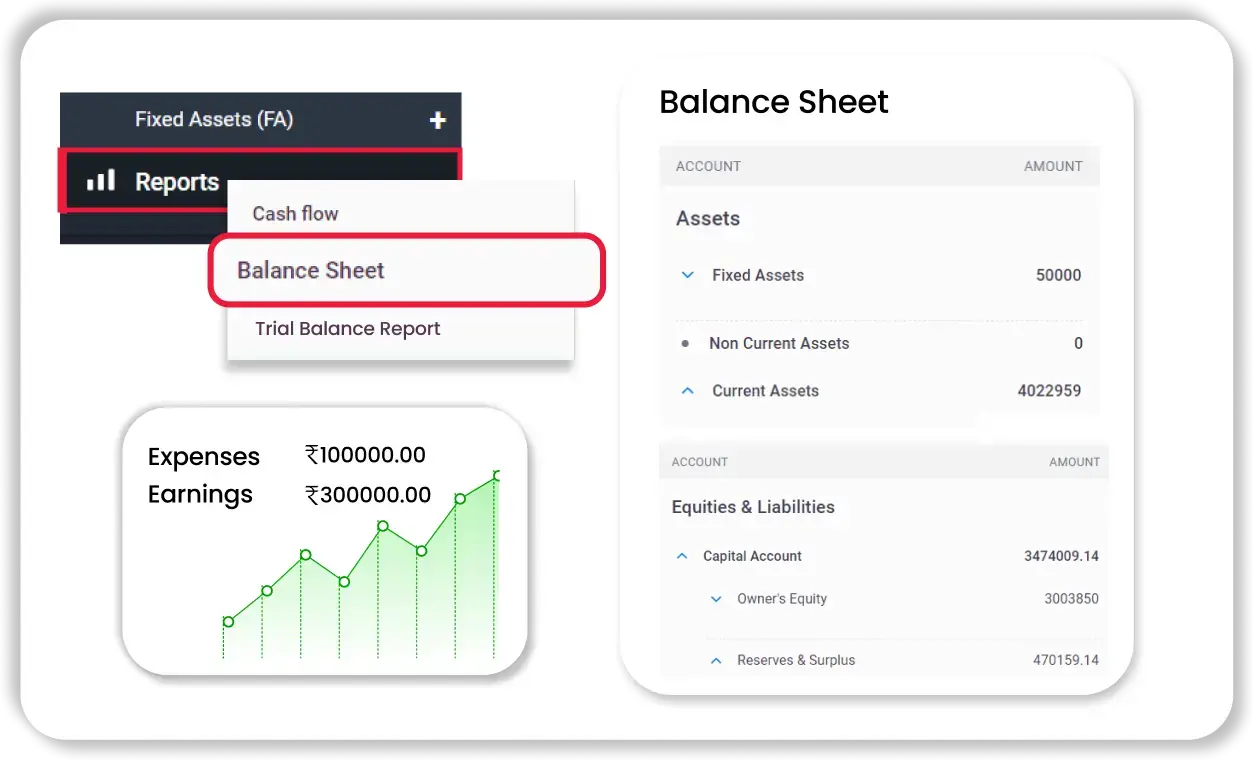
Powerful Reporting Tools
Gain clear financial insights beyond traditional Excel or Word balance sheet formats.
- 40+ Business Reports: From Trial Balance to Profit & Loss and GSTR reports—everything is available within the app.
- Cash Flow Insights: Know where your money goes with in-depth tracking of inflow/outflow and pending payments.
- Downloadable Reports: Export balance sheets and reports in PDF, Excel, or print-ready formats for audits or investors.
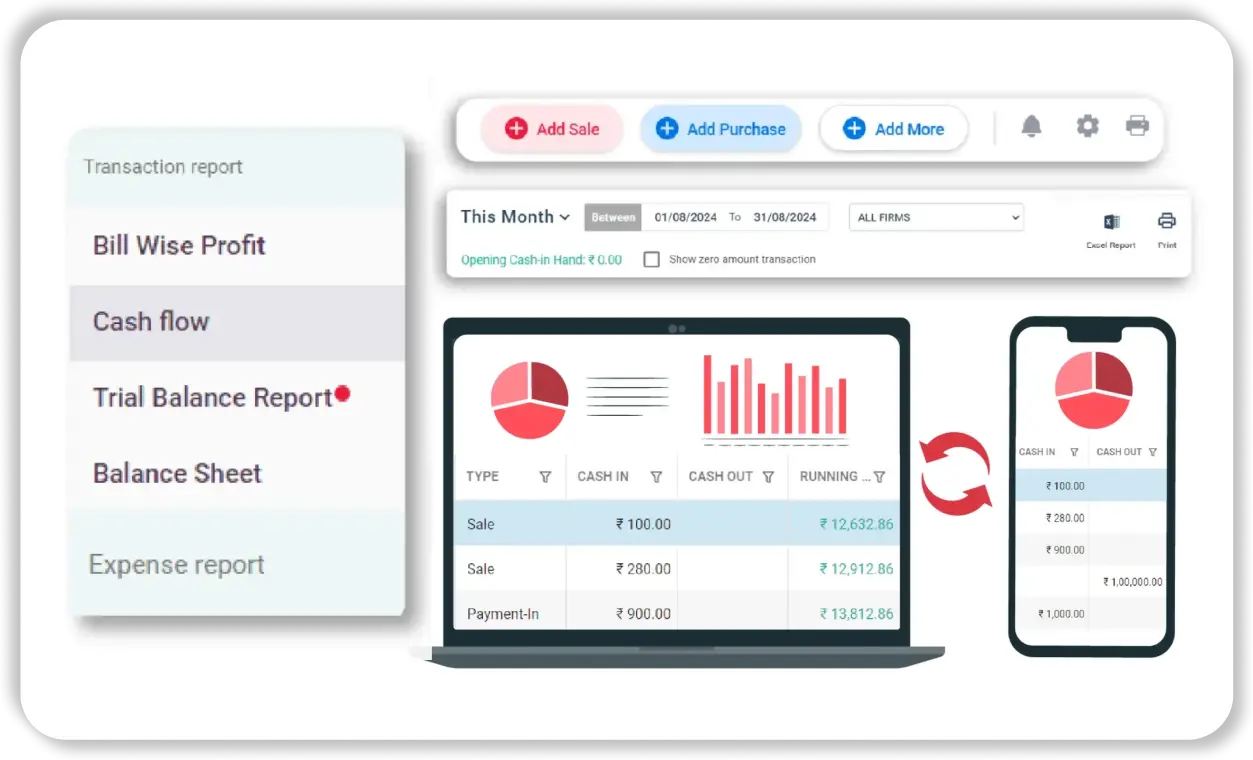
Real-Time Access and Multi-Device Sync
Vyapar works across Android and Windows devices—even offline—making it reliable in all scenarios.
- Offline Functionality: Continue accounting in remote areas or during network outages—data syncs once online.
- Cloud Backups: Safeguard your financial data with automatic backups to Google Drive.
- Multi-Device Sync: Access the same balance sheet across multiple devices with synced updates.
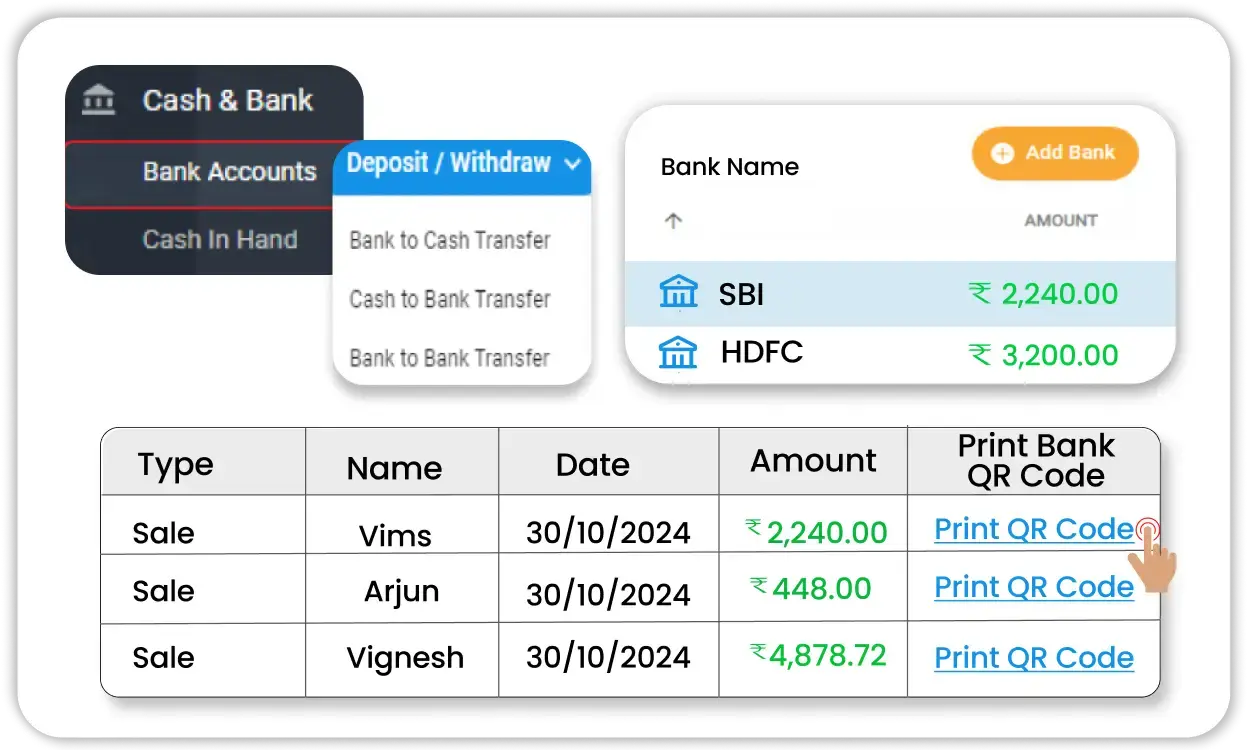
Bank & Cash Account Management
Vyapar helps you track every rupee with integrated banking features.
- Bank Reconciliation: Match your ledger with actual bank statements to prevent accounting errors.
- Multiple Account Tracking: Manage cash, current, savings, UPI, or e-wallet accounts in one place.
- Easy Withdrawals & Deposits: Record deposits/withdrawals and reflect changes instantly in your balance sheet.
Data Safety and Security
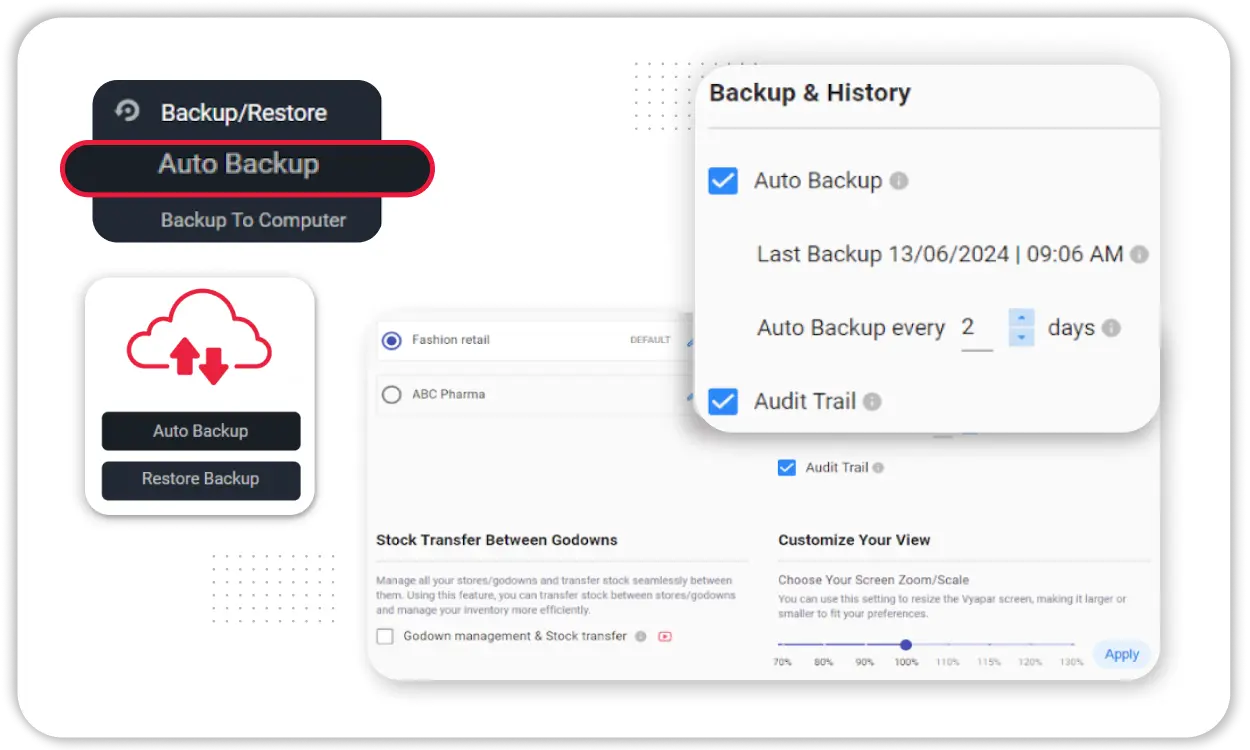
Vyapar ensures your financial data is protected with advanced safety features.
- Automatic Backup on Cloud: Enable auto-backup to Google Drive, ensuring your balance sheets and accounting data are never lost.
- Encrypted Access: All data shared within the app is encrypted, protecting your business from unauthorized access.
- User-Level Control: Restrict access to sensitive financial information by assigning role-based permissions to your team members.
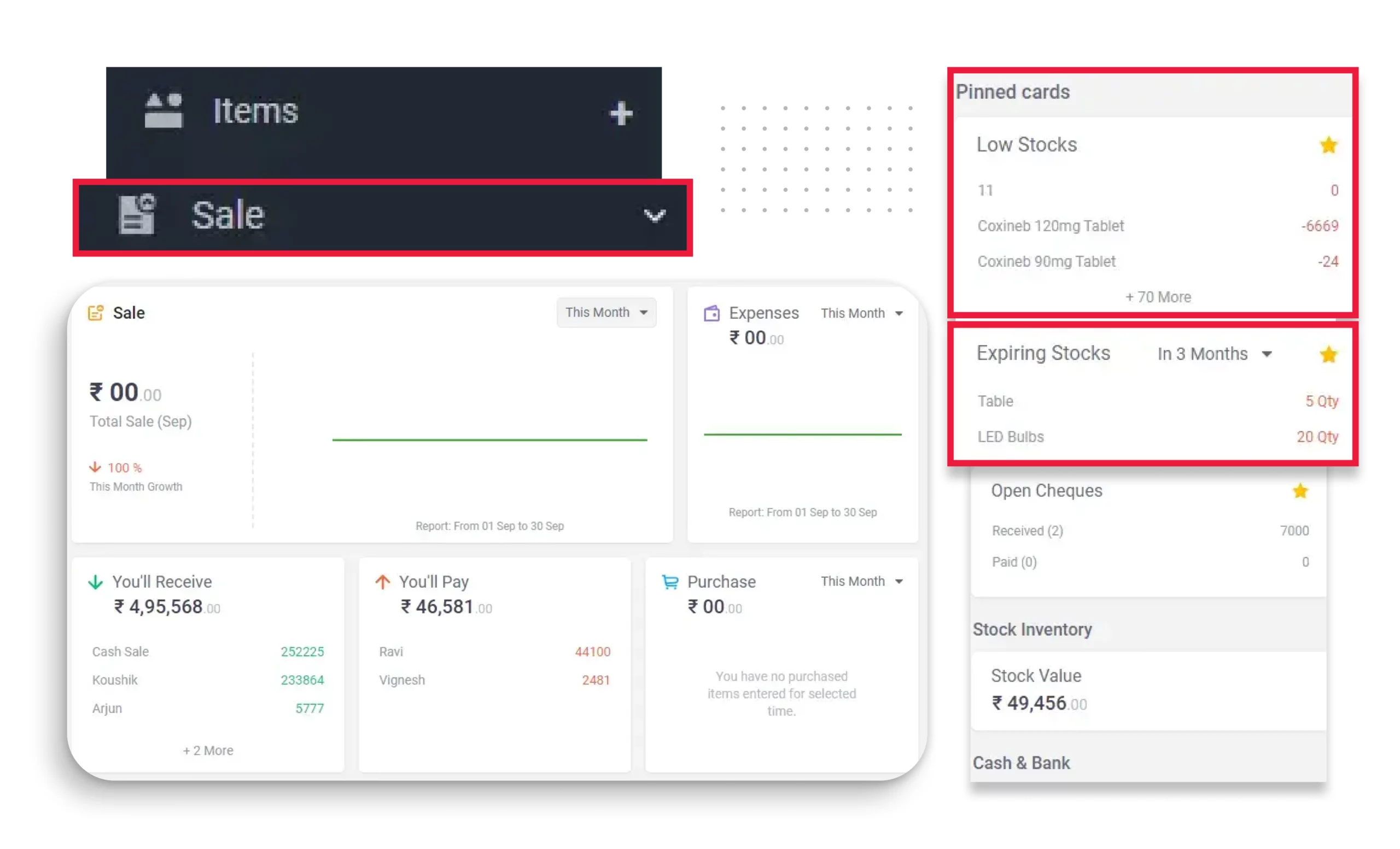
Dashboard Management
Get a complete bird’s-eye view of your finances with Vyapar’s intelligent dashboard.
- Real-Time Business Snapshot: Instantly check your bank balance, stock levels, outstanding payments, and cash in hand.
- One-Click Access to Reports: Download your latest balance sheet, profit & loss, or tax reports directly from the dashboard.
- Visual Charts & Graphs: Make data-driven decisions with visual insights on expenses, income, and liabilities at a glance.
Features of Balance Sheet
Here are some useful features of a balance sheet:
- Financial Health Check – Provides a clear picture of your business’s overall financial position, helping you assess stability and growth potential.
- Performance Evaluation – Helps analyze financial performance by identifying strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
- Strategic Planning – Offers valuable insights into assets, liabilities, and equity, enabling informed decision-making for future investments and expansions.
- Business Sustainability – Determines a company’s ability to meet short-term and long-term financial obligations, ensuring long-term viability.
- Investor Trust – A well-structured balance sheet boosts investor confidence by demonstrating financial stability, profitability, and transparency.
- Regulatory Compliance – Ensures businesses adhere to accounting standards and legal requirements, maintaining credibility with authorities and stakeholders.
- Liquidity & Solvency Assessment – Helps determine whether a business has enough assets to cover its liabilities, reducing financial risks.
- Loan & Credit Approval – Essential for securing business loans and credit facilities, as lenders evaluate the balance sheet before approval.
- Growth Monitoring – Tracks financial progress over time, allowing businesses to compare past and present performance to set realistic future goals.
Are you a Business Owner?
Take your business to the next level with Vyapar!
Try our Android App (FREE for lifetime)
Varieties of Balance Sheet Formats

Balance Sheet Format in Excel With Formulas:
Excel spreadsheets offer a structured way to organize balance sheet entries by categorizing assets and liabilities for better clarity. With built-in calculation formulas, they simplify complex financial computations.

Balance Sheet Formats in Word:
Word-format balance sheets offer a simple yet professional solution for businesses. Vyapar provides customizable MS Word formats, allowing you to tailor them to your needs. Easily edit, embed tables, and present data in a structured, professional manner.

Balance Sheet Formats in PDF:
PDF balance sheets offer a fixed, reusable format for consistency. With Vyapar, you can customize and standardize your balance sheet layout, ensuring uniformity across branches. This simplifies accounting and data management for your business.

Balance Sheet Formats in Google Sheets:
Save time on recurring balance sheets with balance sheet accounting software. Vyapar offers a variety of built-in Google Sheet formats, which are easy to use, customizable, and accessible across all devices.

Balance Sheet Formats in Google Docs:
Vyapar offers a variety of customizable balance sheet formats compatible with Google Docs and Google Sheets. Easily modify them to suit your business needs and clearly present assets and liabilities in a structured format.

Balance Sheet Formats for Start-Up Business:
Startups benefit from pro forma balance sheets to track assets, liabilities, and net worth over time. This helps in securing funding, assessing growth, and identifying financial concerns for better planning.

Balance Sheet Formats for Non-Profit Organizations:
Vyapar’s customizable balance sheet formats help non-profits track assets, liabilities, and equity efficiently. Easily reusable, they simplify annual reporting, saving time and costs. Compatible with Excel, Google Sheets, and cloud storage.

Balance Sheet Formats for Small Business:
Small businesses need industry-specific balance sheets to track growth and stability. Vyapar helps monitor liabilities, manage working capital, and assess business longevity. Easily compare performance with past years for better planning and success.

Balance Sheet Formats for Self-Employed:
A self-employed balance sheet tracks owner’s equity, assets, and liabilities at a specific date. Unlike corporate sheets, it focuses on owner’s equity instead of shareholders’ equity. Vyapar simplifies and speeds up balance sheet creation, saving time and effort.

Company Balance Sheet Format:
A company balance sheet format offers a structured layout to assess financial health, detailing assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a specific point in time.
Vyapar’s Growing Community
Are you a Business Owner?
Take your business to the next level with Vyapar!
Try our Android App (FREE for lifetime)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs’)
1. Business Snapshot or the statement of financial position in terms of assets and liabilities
2. Determining risks and returns by analysing the short-term and long-term impact of your current financial condition
3. Securing loan and other capitals based on the businesses requirements and earning potentials
4. Providing financial ratios by understanding operational efficiency, profitability, and liquidity.
A balance sheet helps in describing organization’s financial health insightfully and professionally. It reveals the liabilities and assets of a business to the interested parties,thereby giving an idea of the shareholders’ equity at any point in time.
Balance sheets are used by anyone interested in understanding the financial health of abusiness, including existing and potential investors, competitors, company management, and government agencies.
A strong balance sheet goes beyond merely listing down assets and liabilities of a business. It possesses various attributes, including cash flow, working capital, income-generating assets, and a balanced capital structure.
A balance sheet consists of financial report of an organization’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder’s (owner’s) equity. It helps evaluate the capital structure of a business.
Off-balance sheet items are assets and liabilities that are excluded from the balance sheets of an organisation. These are not directly owned by a business or are not in the direct obligation of a company.
A balance sheet is often referred to with terms “statement of financial position” or “statement of financial condition” in financial accounting.
The fundamental equation of a balance sheet is:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
A balance sheet represents a snapshot of an organization’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at any particular point of time. An income statement talks about the company’s revenue and expenses during a specific period.
The vertical balance sheet format is the new balance sheet format as per the Companies Act 2013. It lists the equities and liabilities on the top, followed by the assets at the bottom. The new form is mandatorily applicable to all companies except insurance, banking, and electricity companies.
The essential terms used in a balance sheet are Assets, Liabilities, Capital, and Shareholder’s Equity.
A balance sheet is a snapshot of the financial activities of the business. Assets are what you own, liabilities are what you owe, and capital refers to the company’s finance.
The balance sheet is broken into two main areas. The first section consists of equities and liabilities, and the second section includes assets. Accounts are categorised by the liquid status of their assets and liabilities.
The form of the balance sheet is Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity. When the aggregate value of the liabilities and shareholders’ equity equals the value of the assets, the balance sheet is in balance.
In the asset section, you can show items like cash, stock, debtors, investments, prepaid expenses, and fixed assets.
The liabilities include long-term debt, short-term debt, creditors, provisions for doubtful accounts, and outstanding liabilities.
The owner’s equity contains share capital, retained earnings, and additional paid-up capital.
The balance sheet gives a summary of a company’s current financial situation. The balance sheet follows the accounting equation Assets=Liabilities+Shareholders’ Equity. It implies that a business must either borrow money to cover all of its assets (assuming liabilities) or raise money from investors (issuing shareholder equity).
Any share capital except common shares, convertible securities, or options means other equity. It includes retained earnings, contributed surplus, treasury stock, additional paid-up capital, and other items.
Balance sheets are an essential piece of financial information. Every business owner must understand the balance sheet to monitor their company’s financial health. Balance sheets with income and cash flow statements provide owners with the financial data necessary to make informed decisions.
Firstly, find the net value of all fixed assets. Next, add capital investments and current assets. Lastly, subtract the liabilities, and you will get the total capital. The formula for the same is Capital=Assets-Liabilities.
Liabilities=Assets-Owners Equity is the formula to find the total liabilities. You can also add long-term and short-term liabilities to find the total liabilities.
Sales are generally written in a trading account and are not a part of the balance sheet because a balance reflects what you have, not what you sold. However, sales affect the balance sheet because it generates revenue, thus increasing the company’s assets.
An asset is something that a company owns with the expectation it will provide financial benefits in the future. The classification of assets includes tangible and intangible assets. Further, there are two types of tangible assets: current and fixed.
There are several types of balance sheets available. The most common formats are common-sized, comparative, and vertical balance sheets.
The balance sheet adheres to the following equation: Assets=Liabilities+Owner’s Equity. Both sections of the balance sheet must tally.
The separate elements of owner’s equity, such as dividends, shareholder capital, revenue, and expenses, are included in the expanded accounting balance sheet. The extended equation can compare a company’s assets at a more acceptable level than the basic equation.
The Accounting Equation’s left and right sides are always equal because every asset a business owns has been acquired solely from the funds its owners and creditors supply. If both sides do not tally, the report is not accurate and fair.
On the balance sheet, any profits not paid out as dividends are shown in the retained profit column. Any profit or net income belongs to the owner of a sole proprietorship or a corporation’s stockholders.
The balance sheet shows the closing balance of the capital.
There are two sides to a balance sheet: assets on the left and liabilities on the right. Further, both sides have their sub-classification.
The capital invested in a business has a credit balance and is listed on the liabilities side of the balance sheet since it is used to pay off all obligations accrued.
The double entry principle in accounting is the main factor causing a balance sheet to tally. Since every transaction is recorded in at least two different accounts, this accounting system also serves as a check to ensure that the entries are accurate.
The assets of your business should equal the liabilities and equity of your business on the balance sheet. If it does not tally, your balance sheet is not balanced and has some mistakes.
Executives, investors, analysts, and regulators utilise the balance sheet as a crucial tool to comprehend the current financial condition of a corporation. It frequently coexists with the income and cash flow statements, the other two categories of financial statements.
The balance sheet does not include revenue because the profit and loss statement records the income. The P&L tracks how much money the company makes or loses.
A balance sheet is valuable for all the stakeholders to make informed decisions. In addition to listing the company’s assets and liabilities, a balance sheet provides interested parties with information about the company’s financial status.
The basic format of a balance sheet includes three main sections: assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets list resources owned, liabilities outline obligations, and equity shows net worth or ownership.
This formula represents the fundamental accounting equation, which states that a company’s assets are financed by its liabilities and equity. In other words, the resources owned by the company (assets) are either provided by creditors (liabilities) or the owners/shareholders (equity). This equation must always balance, ensuring that the company’s financial position is accurately reflected on the balance sheet.
The balance sheet formula is: Assets = Liabilities + Equity
To prepare a balance sheet:
1. Gather financial information on assets, liabilities, and equity.
2. Organize assets into current and non-current categories.
3. List liabilities, including current and non-current obligations.
4. Calculate equity by subtracting liabilities from assets.
5. Format the balance sheet with assets on the left and liabilities plus equity on the right.
6. Check for accuracy and ensure the balance sheet equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) balances.
7. Review and interpret the balance sheet for financial insights.















