Balance Sheet Format as per Companies Act 2013 in Excel, Pdf
Get compliant & error-free balance sheets as per companies Act 2013 with Vyapar App. Generate, track & manage them instantly.
⚡️ Eliminate errors with pre-defined formulas
⚡ Simplify calculations and save time
⚡️ Generate accurate balance sheets in minutes

Download Free Balance Sheet Format as per Companies Act 2013
Download the Balance Sheet Format as per Companies Act 2013 in Excel, Pdf, and make customization according to your requirements at zero cost.


Customize Invoices

Balance Sheet Format as per Companies Act 2013 Type I
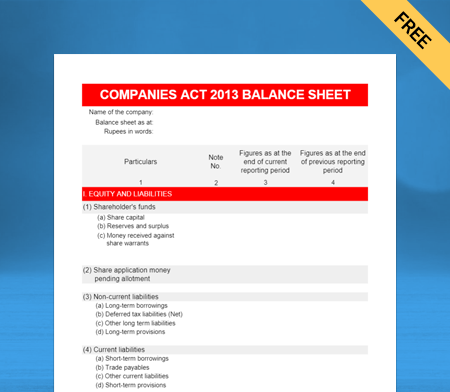
Balance Sheet Format as per Companies Act 2013 Type II
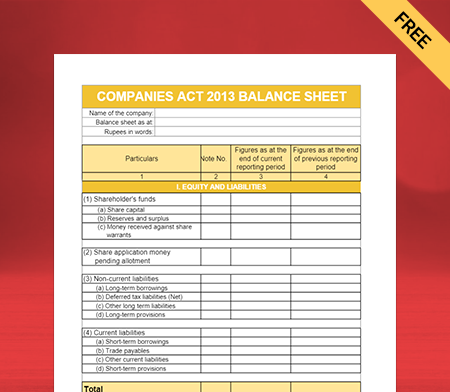
Balance Sheet Format as per Companies Act 2013 Type III

Balance Sheet Format as per Companies Act 2013 Type IV
Generate Invoice Online
Highlights of as per Companies Act 2013 Balance Sheet Simple Templates
We’ve put in a lot of effort to make sure you get the best template possible

All versions are print friendly

Built From scratch

Include essential invoice elements

Automatically calculate subtotal and grand total amounts

Consistently formatted
What is a Balance Sheet Format As Per Companies Act 2013?
All companies must maintain a vertical balance sheet as per section 129 of the Companies Act 2013. A vertical balance sheet is several columns beginning with liabilities and capital followed by all the assets.
It gives a snapshot of an organisation’s solvency, profitability, and liquidity. There are two ways to present the assets and liabilities accounts: Based on liquidity or permanence. The primary purpose of a vertical balance sheet is for the user to compare different figures for a given time.
Components Of a Balance Sheet Format as per Companies Act 2013:

Assets
Current Assets:
Current Assets are the short-term assets of a company that expects to be sold, consumed, used, or exhausted within one year through business operations. They are also known as current accounts and are essential for running a business. They include attributes like cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivables, marketable securities, stock inventory, and other liquid liabilities.
The current ratio indicates a company’s liquidity, calculated by dividing existing assets by current liabilities. It reveals the ability of the company to meet short-term obligations. Similarly, the quick ratio measures the power of a company to use its near cash assets to extinguish its current liabilities immediately.
Fixed Assets:
Fixed Assets are long-lived assets, tangible assets, or property that a business cannot convert into cash quickly. Also known as Non-Current Assets, they take a significant amount of time to liquidate and are used to generate revenue during business operations. The company can use them to get credit and attract investors as they hold long-term values.
Fixed Assets are investments and are a solid indicator for the stakeholders that the company has growth potential. They are of two types: Freehold and Leasehold Assets. Freehold assets are purchased with legal rights of ownership and use, while the Owner uses leasehold Assets without the legal right for a particular period.
Liabilities
Current Liabilities:
The current liabilities are the company’s short-term financial obligations that the business will settle in cash within the company’s operating cycle. The tenure of current liabilities lies within the same year, and the user can pay them using current assets within that calendar year.
Current Liabilities include dividends payable, accounts payable, short-term debts, and income tax. The current liabilities ratio to current assets helps determine the company’s ability to repay the short-term debts. It shows the management capabilities of a business, thus grabbing the immediate attention of the investors.
Long-term Liabilities:
Long-term Liabilities are the debts a company owes to third-party creditors that are payable beyond a year. They represent an organization’s long-term financial obligations due with tenure over a calendar year and do not require immediate clearance.
The standard operation period is known as the time it takes for a company to turn inventory into cash. Some non-current liabilities include bond payables, deferred tax liabilities, loans against machinery or land, and other long-term mortgages. The long-term liabilities give a better idea of the company’s current liquidity and help manage the business.
Shareholder’s Equity
The Shareholder’s equity, also called net worth, is the business’s value after all the liabilities are subtracted from the business’s assets. The basic formula is Owner’s equity = Assets – Liabilities. It shows how much the company owner has invested in the entity, either by investing money or retaining earnings over time.
The phrase “owner” is used for a sole proprietorship, while “shareholder’s equity” is used if the business is incorporated under the companies act 2013. The Owner’s equity is an asset of the business and not the company. If the net worth is negative, additional investments must cover the shortfall.
Create your first invoice with our free Invoice Generator
Other Features of Vyapar Balance Sheet Format As Per Companies Act 2013
Dashboard Management
The Dashboard of the Vyapar free billing software helps you check your business status, and you can easily track your business data and information across all areas of the entity. The Dashboard is user-friendly, which makes it easy to use. By clicking on the left corner of the app, you can add company details and print those details in invoices with the correct settings. You can find out about cash-in-hand, bank balance, stock, and other crucial information about your entity’s financial health in one place.

Data Safety and Security
The accounting and invoicing software handles data and ensures that it’s safe with the help of three aspects. They are Login security, Data Encryption, and Continuous backup. The Vyapar free accounting App helps you take backup of the data in your google drive, which you can do by enabling Auto Backup. The software is bound to guard user privacy so no one can access the user’s data, not even Vyapar itself. We recommend changing passwords at intervals and keeping the backups offline for safety.
Bank Accounts
Companies can easily add, manage, and track the payments more quickly by using the free accounting and billing software of Vyapar. Vyapar supports multiple modes of payments, so you can easily enter the data whether your revenue is from banks or e-wallets. It is an efficient way to manage the accounts, but you must add your bank with the Vyapar software. Also, you can access the data from anywhere with internet connectivity.


Business Reports
After creating invoices, you can use the collected data to create a balance sheet and sales or purchase reports quickly to analyze different metrics of the growth of your business. You can create various reports like inventory reports to identify product demand and focus on keeping stock of them in-store. A tax statement can help you in filing taxes and GST seamlessly. Also, you can eliminate lots of manual work and save time for your employees. You don’t need to hire employees, eliminating extra costs.
Benefits of using Vyapar Balance Sheet Format as per Companies Act 2013
Offline Access:
Most accounting software relies on internet connectivity, making it difficult to use them in remote areas. With Vyapar App, you don’t have to worry about internet access or connectivity as it is an offline application, and you can easily use it anywhere. Also, the offline feature ensures the safety of your data, which keeps it accessible only to the user, and third parties and even Vyapar can not access it.

Saves Time:
Manual bookkeeping is a time-consuming process, and it takes a lot of time to ensure that all the data is correct. The Vyapar app automatically records all your transaction data and generates reports. You can quickly review the statements and analyze your business. Anyone in your team can manage the software, so you don’t need to hire extra staff for the particular task.
Easy to use:
You don’t need any special accounting knowledge to use the Vyapar software. Its user-friendly interface makes the app easier to operate, and you can instantly access the data from mobile to desktop and desktop to mobile. Also, the Vyapar accounting software is compatible with all small and medium-sized businesses. The user can use Vyapar for GST registered or unregistered entities, and it will generate GST-related reports.

Customization:
Using the Vyapar app, you can create and print invoices for your business with 12 various customisable invoice themes. The financial records must be accurate, properly formatted, and delivered on time when dealing with stakeholders. You can share your brand invoices with your brand logo, making you look more professional. The new feature of Vyapar allows you to export data from the Vyapar to Tally directly.
Reduces Errors:
The Vyapar app uses tools that automatically update your transactions’ data as they happen. Thus it decreases the chances of errors and mistakes. It also gives you information about what has been sold and what you need to restock. Manual data entry is inclined to error and can harm your business, and Vyapar is an easy way to get accurate and real-time information.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs’)
Balance provides a snapshot of business in terms of assets and liabilities and helps determine risk and returns by analyzing your current financial condition’s short-term and long-term impact. It also provides financial ratios by understanding operational efficiency, profitability, and liquidity.
A balance sheet format as per companies act 2013, helps describe an organization’s financial health insightfully and professionally. It reveals the liabilities and assets to the stakeholders, thereby giving an idea of the shareholders’ equity at a specified time.
Anyone interested in understanding a company’s financial health, including existing and potential investors, opponents, managers, and government agencies, can use balance sheets.
A strong balance sheet goes beyond just listing down the assets and liabilities. It contains various details, such as cash flow, income-generating assets, working capital, and a balanced capital structure.
Any balance sheet format contains details of an organization’s financial health insightfully and professionally. It consists of a financial report of its assets, liabilities, and net worth. Further, it helps assess the capital structure of a business.
The balance sheet format as per the Companies Act, 2013, is a standardized format for presenting financial information about a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. It includes sections for assets (current and non-current), liabilities (current and non-current), and equity components such as share capital and reserves. This format aims to ensure transparency and accuracy in financial reporting, providing stakeholders with a clear snapshot of the company’s financial position.
The format of the balance sheet as per the Companies Act, 2013, includes sections for Equity and Liabilities (Shareholder’s Funds, Non-Current Liabilities, Current Liabilities) and Assets (Non-Current Assets, Current Assets). Additionally, there are Notes to Accounts for detailed explanations and disclosures. This vertical presentation aims to provide a clear view of the company’s financial position.
The structure of the balance sheet as per the Companies Act, 2013, includes two main sections: Equity and Liabilities (Shareholder’s Funds, Non-Current Liabilities, Current Liabilities) and Assets (Non-Current Assets, Current Assets). This format follows a vertical presentation, making it easier to understand the company’s financial position.
The schedule of the balance sheet as per the Companies Act, 2013, includes sections for Equity and Liabilities (Shareholder’s Funds, Non-Current Liabilities, Current Liabilities) and Assets (Non-Current Assets, Current Assets).
As per the Companies Act, 2013, companies in India are required to follow the format for financial statements prescribed in Schedule III of the Act. This format provides guidelines and requirements for preparing balance sheets, profit and loss accounts, and other financial statements in a standardized manner. It aims to promote transparency, comparability, and accuracy in financial reporting, ensuring that stakeholders have clear and reliable information about a company’s financial performance and position.
Under the Companies Act, 2013, the audit of financial statements involves an independent examination of a company’s financial records and statements by a qualified auditor. This includes assessing compliance, verifying transactions, and issuing an audit report expressing an opinion on the fairness and accuracy of the financial statements.





