Table of Contents
- History and Background of GST
- The Old Tax Rules Before GST
- Objectives of the Goods and Services Tax
- Types of Goods and Services Tax
- GST Registration: Is Your Business Eligible?
- Documents Required for GST Registration
- How to Register for Goods and Services Tax
- When to File GST Returns
- Benefits of the Goods and Services Tax
- What are GST Rates and Slabs
- How Goods and Services Tax Is Calculated
- Impact of GST on the Supply Chain
- Role of Tax Authorities in GST Compliance
- Why GST Matters to Business Owners
- How to manage Goods and Service Tax in Vyapar App
- FAQ’s
What Is GST(Goods and Services Tax)? A Simple Guide
Estimated reading time: 13 minutes

Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a tax that businesses add to the price of goods and services in India. This unified tax system replaced multiple older taxes, making it easier for both businesses and customers. When a business sells products or offers services, it collects this tax from the customer and pays it to the government. By having the same rate across the country, GST creates a fair and straightforward tax structure.
History and Background of GST
The implementation of GST took place on July 1, 2017, marking a major change in India’s tax system. Before the Goods and services tax, businesses had to handle many taxes.
These included VAT (Value Added Tax), service tax, excise duty, and entry tax. These taxes varied from state to state, making tax management complicated and costly. The government introduced a Goods and services tax to replace many taxes. This aims to create a single indirect tax system that is simple and uniform across India.
The Old Tax Rules Before GST
Earlier, India’s tax system had multiple layers:
- VAT (Value Added Tax): Collected by each state on goods.
- Service Tax: Charged by the central government on services.
- Excise Duty: Tax on goods manufactured in India, collected by the central government.
- Entry Tax: Tax on items coming into specific states.
Each tax had its own rules and rates, making it difficult for businesses to operate across multiple states. The Goods and Services Tax simplified this by combining all these taxes into one.
Objectives of the Goods and Services Tax
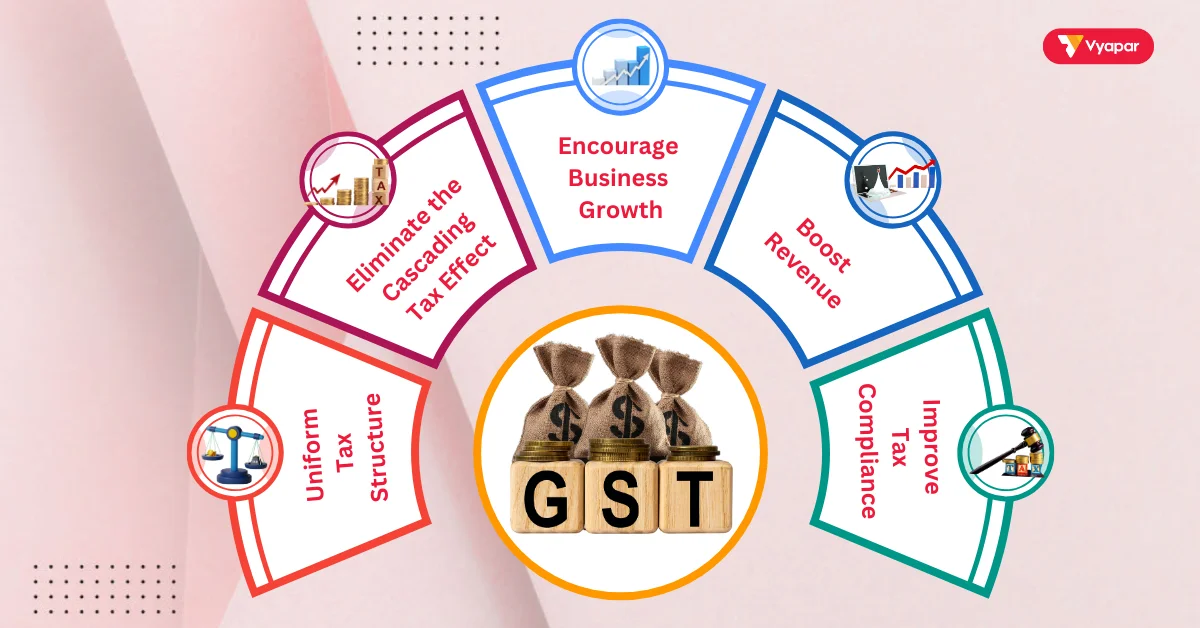
The government introduced Goods and service tax with several main goals:
- Uniform Tax Structure: Goods and Services Tax combines multiple taxes into one, making it easier for businesses and customers to understand.
- Eliminate the Cascading Tax Effect: Goods and Services Tax removes the “tax on tax” issue. This lowers the overall cost of goods and services.
- Encourage Business Growth: A single tax rate across states makes it easier for businesses to expand nationwide.
- Boost Revenue: The streamlined structure helps reduce tax evasion, increasing government revenue.
- Improve Tax Compliance: A transparent tax structure aids companies in comprehending tax regulations. Tax regulators establish these rules. The GST contributes to this endeavor.
Types of Goods and Services Tax
To manage tax collection effectively, GST is divided into four main types:
- Central GST (CGST): Collected by the central government for sales within a state.
- State GST (SGST): Collected by the state government on sales within that state.
- Integrated GST (IGST): Collected by the central government on sales between different states or interstate supplies.
- Union Territory GST (UTGST): Collected in Union Territories like Delhi and Chandigarh.
This division makes sure that both central and state governments get their share of GST revenue. This keeps tax collection balanced and fair.
GST Registration: Is Your Business Eligible?
To sell goods or provide services in India, a business must register for Goods and service tax. You must meet this requirement if your annual turnover exceeds the threshold limit. Here’s how the limit works:
- Businesses with an annual turnover above ₹40 lakh must register for Goods and service tax.
- Any services with an annual turnover above ₹20 lakh must register for Goods and service tax.
Once registered, each business receives a unique GST Identification Number (GSTIN). This number helps the government track tax payments.
Documents Required for GST Registration
To register for the Goods and Services Tax, you’ll need to provide some key documents:
- PAN Card of the business owner.
- Aadhar Card for identification in India.
- Proof of Business Address (such as a rental agreement or electricity bill).
- Bank account details, such as a cancelled check.
- Digital Signature for verification.
These documents confirm the business’s identity and make it easier for the government to maintain accurate records.
How to Register for Goods and Services Tax
You can complete the simple registration process for Goods and service tax online. Here’s a quick guide:
- Visit the GST Portal: Go to the official Goods and service tax website.
- Select “New Registration”: Enter your PAN, phone number, and email.
- Fill Out Business Details: Provide information such as business name, address, and bank details.
- Upload Necessary Documents: Upload required documents like PAN and proof of business address.
- Verify Details: Complete verification using OTP and digital signature.
- Receive GSTIN: After approval, you will get a Goods and Service Tax Identification Number (GSTIN).
This unique GSTIN allows your business to legally collect and pay taxes.
When to File GST Returns
Filing GST returns is mandatory for all registered businesses. GST returns are reports that show the income, expenses, and tax collected or paid by a business. Depending on your business type, returns must be filed monthly, quarterly, or annually. Here’s an overview:
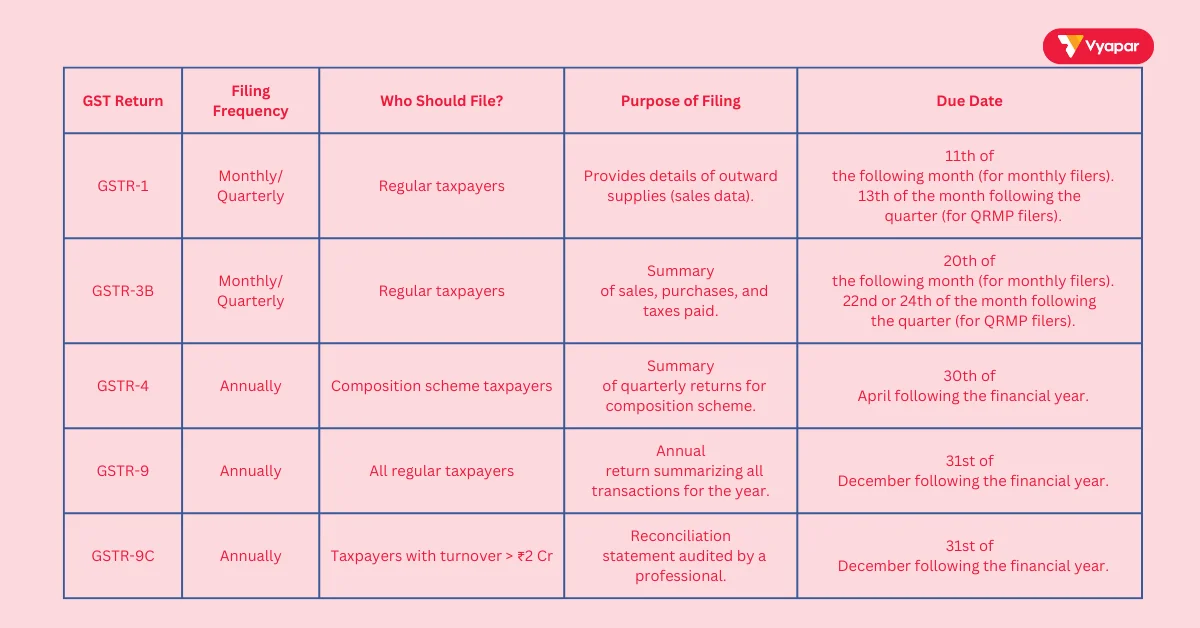
- Monthly GST Returns: Regular taxpayers must file GSTR-1 (sales data) and GSTR-3B (summary of transactions) every month.
- Quarterly Returns: For businesses under the Quarterly Return Monthly Payment (QRMP) scheme, GSTR-1 can be filed quarterly.
- Annual GST Return: Registered businesses must also file GSTR-9, summarizing all transactions for the year.
Late filing of GST returns can lead to penalties and interest on unpaid taxes.
Benefits of the Goods and Services Tax
The Goods and Services Tax brings multiple benefits for businesses and customers:
- Simplified Tax System: GST combines different types of taxes into one. This makes it easier to understand and manage.
- Reduces Tax Evasion: With clear rules, it’s harder for businesses to avoid paying taxes.
- Encourages Growth: The same tax rate across all states simplifies cross-state business.
- Transparent Pricing: With goods and service tax, customers can see the exact tax they are paying, creating trust.
- Improved Compliance: GST laws are straightforward, helping businesses to stay compliant with tax rules.
What are GST Rates and Slabs
In India, GST is charged at different rates depending on what you sell. If you’re under the Regular GST Scheme, the main tax slabs are 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.
Basic items like fresh food often fall under 0%, while everyday goods and services are usually taxed at 5% to 18%. Luxury items like cars and tobacco may be taxed at 28% or more.
If you choose the Composition Scheme, GST is much simpler. You pay tax at a fixed rate on your total sales: 1% for traders and manufacturers, 5% for restaurants, and 6% for service providers. This helps small businesses stay compliant without dealing with complex tax rules.
Here’s a summary:
- 0% GST (Exempt): Basic items like food grains and essential medicines are tax-free to remain accessible.
- 5% GST: Covers common items such as pre-packaged food, tea, and cooking oils to maintain low prices.
- 12% GST: Applies to items like mobile phones and processed foods, balancing between necessity and luxury.
- 18% GST: The standard rate for goods and services like personal care items, restaurant bills, and household appliances.
- 28% GST: Imposed on luxury goods such as cars, air conditioners, and high-end electronics.
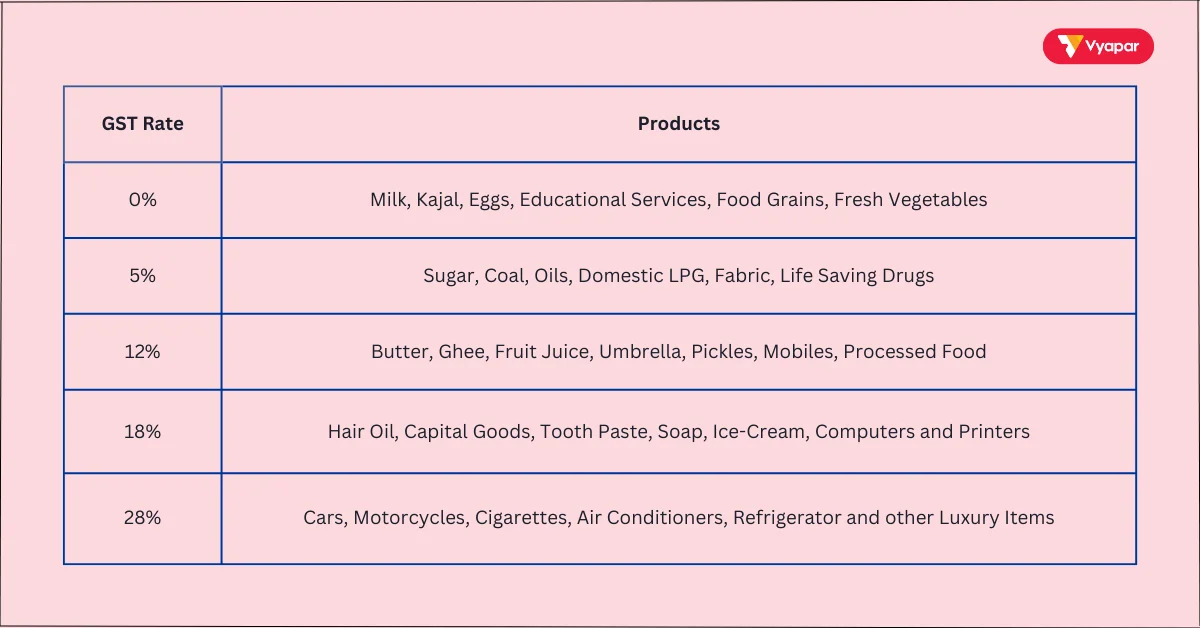
This structure helps support fair pricing, with essentials taxed lower and luxury items taxed higher.
How Goods and Services Tax Is Calculated
GST is calculated based on the price of goods or services sold. The seller adds the tax amount to the original price, resulting in the final price the customer pays. Here’s the formula:
GST Amount= (Original Price × GST Rate)/100
Then,
Final Price= (Original Price + GST Amount)
For example, if an item costs ₹100 and falls under the 18% tax rate:
- GST Amount = (100×18)/100=18
- Final Price = 100 + 18 = ₹118
This simple formula helps businesses calculate the total cost, including taxes.
Impact of GST on the Supply Chain
Before GST, multiple taxes were applied at different points in the supply chain, leading to higher costs. The unified tax system lets businesses pay just one tax. This lowers costs and makes the supply chain faster and more efficient. Now, whether businesses move goods between states or within a state, they apply a consistent tax rate, which reduces delays and costs.
Role of Tax Authorities in GST Compliance
GST compliance is overseen by both central and state tax authorities. They collaborate to ensure businesses register properly, pay the correct tax amount, and file returns on time. The central government collects taxes on interstate sales, while state governments handle intrastate taxes. This cooperation ensures fair tax collection across the country.
Why GST Matters to Business Owners

Understanding the Goods and Services Tax helps business owners make better decisions. Here’s why it matters:
- Easy Compliance: A single tax system makes it easier to follow tax laws.
- Better Pricing: Knowing the tax rates helps set fair prices for products and services.
- Smoother Operations: Businesses don’t have to worry about multiple taxes.
- Improved Cash Flow: With Goods and service tax, input tax credits reduce the overall tax amount, freeing up cash for business growth.
- Transparent Bills for Customers: Showing tax amounts clearly on invoices builds customer trust.
How to manage Goods and Service Tax in Vyapar App
Vyapar App simplifies managing Goods and service tax for small businesses. Here’s how it helps:
- Select Correct Slabs: Vyapar allows you to choose the correct slab for each item, ensuring accurate billing.
- Creates GST-Compliant Invoices: Vyapar generates invoices that meet Goods and service tax rules, including the correct tax rates.
- Automatic Calculations: The app calculates taxes automatically, so there’s no need to do it manually.
- Instant Tax Reports: Vyapar organizes tax reports like GSTR-1, GSTR-2A, GSTR- 3b, GSTR-9. Making it easy to file returns on time.
- Organized Record-Keeping: Vyapar tracks all tax payments and collections, helping businesses with tax compliance.
- Helps with GSTR Filing: Vyapar helps businesses get all the needed information for GST filing. It collects the data required for GST returns in “JSON” file so you’re prepared when it’s time to submit to the tax office.
Using Vyapar apps GST Billing software saves time, reduces errors, and keeps your business compliant with tax laws.
Are you a Business Owner?
Take your business to the next level with Vyapar! Try free!
Try our Android App (FREE for lifetime)
FAQ’s
Goods and Services Tax is a unified tax system applied to goods and services, replacing multiple older taxes.
The government introduced GST to make India’s tax system simpler. It replaces many state and central taxes with one single tax.
Four types exist:
Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST)
State Goods and Services Tax (SGST)
Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST)
Union Territory Goods and Services Tax (UTGST)
You calculate Goods and service tax by multiplying the original price by the GST rate. The calculation is straightforward: (Cost × GST Percentage) / 100.
Documents include PAN card, Aadhar card, proof of business address, and bank account details.
Vyapar automates tax calculations, prepares reports, and helps with GST compliance, making tax management easy.
Related Posts:









