What Is Accounting? A Brief Explanation
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes

What Is Accounting?
Accounting or accountancy is the process of keeping a diary for money. It helps businesses write down and understand all the money they earn and spend. By keeping track of this, companies can see how well they are spending their money.
Purpose of accounting:
The main reason for bookkeeping is to give helpful information about money. This helps business owners see if they are making money, losing money, or just getting by.
How It Works
Basic Process:
- Documenting Financial Transactions: When someone spends or receives money, they write it down. This includes buying things or selling products.
- Financial Classification: We divide financial transactions into categories. These include income (money coming in), expenses (money going out), and other key elements.
- Creation of Financial Statements: The business produces statements illustrating its earnings and expenditures. These include things like profit and loss statements.
- Analyzing Financial Performance: By looking at these reports, businesses can see how they are doing with their money.
Example:
If a shop sells a toy for ₹1,000 and it costs ₹600 to make, the shop makes a profit of ₹400. This implies that the store owner made a profit of ₹1,000 from the sale of the toy. The manufacturing expense amounted to ₹600.
History of Accounting

Ancient Origins:
Accounting has been around for a long time. It started in ancient Mesopotamia, where people wrote on clay tablets to keep track of their goods.
Modern Development:
A smart Italian named Luca Pacioli earned the title of the father of accounting. In 1494, he wrote a book about double-entry bookkeeping, a system that helps businesses record their money. People still use the same method today.
Types of Accounting
Various kinds of accounting help with something special:

- Financial Accounting: This helps make reports for people outside the business, like investors.
- Managerial Accounting: This helps managers inside the business make money decisions.
- Cost Accounting: This shows how much it costs to make a product or provide a service.
- Tax Accounting: This helps businesses prepare their taxes.
- Forensic Accounting: This looks into financial crimes or problems.
- Auditing: This checks the accuracy of financial records.
- Government Accounting: This deals with the money of government agencies.
- Nonprofit Accounting: This helps nonprofit organizations track their money.
- International Accounting: This looks at bookkeeping rules in different countries.
- Environmental Accounting: This report on the environmental costs of business activities.
- Personal Accounting: This helps individuals manage their own money.
- Project Accounting: This tracks the money for specific projects.
Types of Businesses that need Bookkeeping
Every type of business needs bookkeeping, but they all have different needs:
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): They need to track cash flows, follow tax rules and file tax returns. Like local shops and service providers.
- Retail Businesses: They manage inventory and sales, like grocery stores and clothing shops.
- Service-Based Businesses: They keep track of expenses and invoices, like salons and coaching centers.
- Manufacturing Units: They track production costs, like factories making furniture.
- Wholesale Traders: They handle large inventories, like suppliers for hardware stores.
- Healthcare Providers: They manage sales and medical supplies, like clinics and pharmacies.
- Restaurants and Food Businesses: They track sales and manage inventory, like bakeries and food trucks.
- Logistics and Transportation: They manage expenses for things like fuel, and courier services.
- Construction and Real Estate: They track costs and billing, like real estate agencies.
- Fashion Industry: They manage inventory and sales, like clothing brands and accessory designers.
Why It’s Important for Different Businesses:
Bookkeeping helps businesses keep their money organized, follow tax laws, and make smart choices to grow.
Accounting Standards
What Are They?
These standards are rules that businesses must follow when they write their money information. These rules help make sure that everyone reports their money in a similar way.
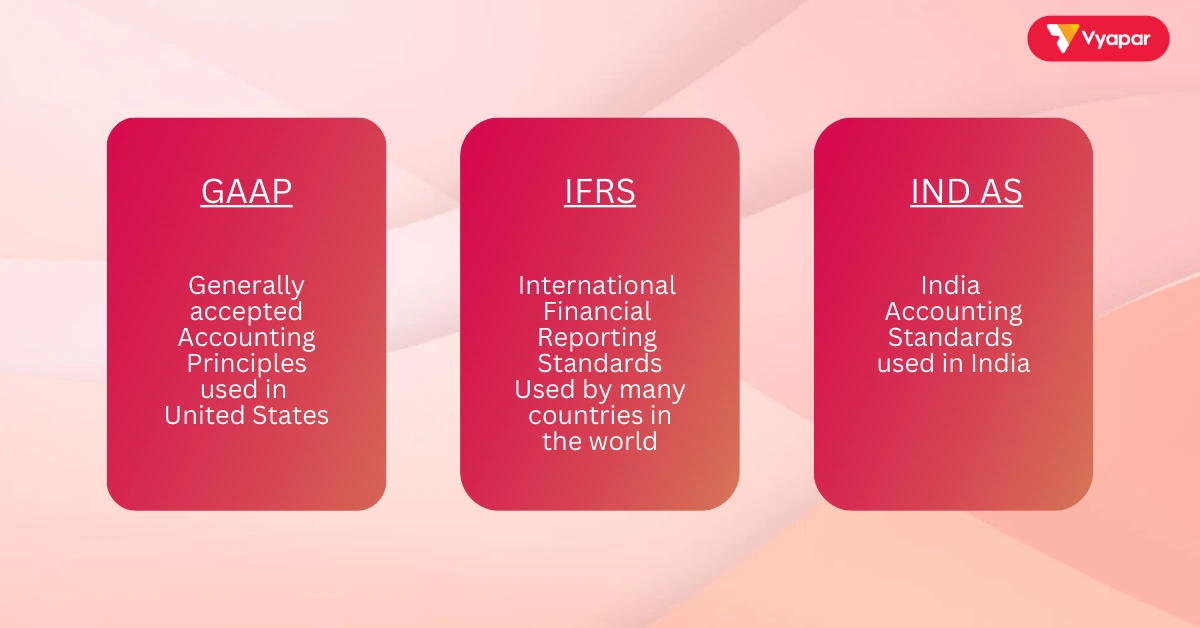
Examples of Standards:
- GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles): Used in the United States.
- IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards): Used in many countries around the world.
- Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS): Used in India.
Importance of Accounting
Why Bookkeeping Matters:
- Financial Tracking and Reporting: Keeping good records helps show how a business is doing.
- Decision-Making: Reliable money data helps businesses make good choices.
- Financial Forecasting and Planning: This helps businesses plan for the future based on past information.
- Tax Compliance: Accurate records help businesses pay their taxes on time.
- Review and Internal Regulations: This builds trust with customers and investors.
- Securing Financing: Good records help businesses get loans or attract investors.
- Performance Measurement and Benchmarking: This helps businesses see how they compare to others in their industry.
- Operational Efficiency: It helps find ways to save money and use resources wisely.
- Long-term Sustainability: This helps plan for future success and Financial position.
- Stakeholder Confidence: Good practices build trust among everyone involved with the business.
Impact on a Business:
Keeping accurate financial records helps businesses avoid money problems and show clear reports to their investors.
Example
Practical Scenario:
Imagine a bakery that buys ingredients for ₹5,000, pays workers ₹3,000, and sells cakes for ₹10,000 in a month. Here’s what it looks like:
- Total Revenue: ₹10,000 (money made from selling cakes).
- Total Expenses: ₹5,000 (ingredients) + ₹3,000 (workers) = ₹8,000.
- Net Income: ₹10,000 (money made) – ₹8,000 (costs) = ₹2,000 profit.
This example helps the bakery owner see if they are making money or not.
How Vyapar App Can Help You
Overview of Vyapar
Vyapar is an app simplified accounting software, that helps small businesses keep track of their money easily. It makes it simpler for owners to focus on growing their business instead of worrying about complicated financial tasks.
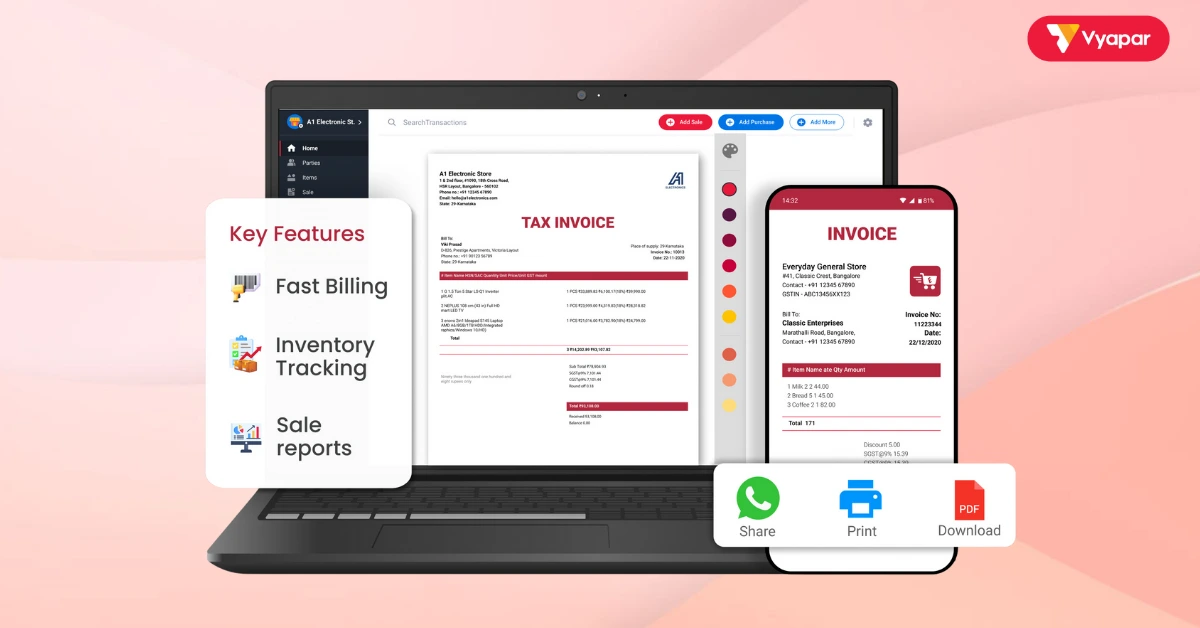
Features and Benefits
- Invoicing: Create easy and professional bills with your business logo.
- Expense Tracking: Write and categorize all expenses, which helps see where money is going.
- GST Compliance: This aids in computing and documenting GST, simplifying and enhancing accuracy for proprietors and certified public accountants.
- Reporting: Easily create financial reports to understand how the business is doing.
- Inventory Management: Keep track of stock and know when to reorder.
- Customer Management: Store customer information and accounts receivable and payable to build better relationships.
- Supplier Management: Keep records of suppliers and manage orders easily.
- Multi-User Access: Allow several people to use the accounting system safely, promoting teamwork.
- Data Security: Protect financial information from unauthorized access.
- Cloud-Based Accessibility: Access Vyapar from any device with the internet.
- Mobile App: Manage financial and bookkeeping tasks from everywhere with the mobile app.
Why Use Vyapar
Vyapar makes bookkeeping easier by automating tasks, reducing mistakes, and providing clear financial information, all at a low cost. User-friendly and offering support, the system helps business owners make better business decisions.
FAQ’s
A surplus is the extra money left after paying all expenses. The additional money a company has.
Financial reporting includes all aspects of tracking money activities, making reports, helping with taxes, and analyzing financial information.
An accounting year is a 12-month period businesses use to prepare financial reports. It can be the same as the calendar year or a different year.
Tax accounting is figuring out how much tax a business needs to pay based on its income and expenses.
GST (Goods and Services Tax) is a tax on the sale of goods and services. Businesses must collect the right amount and pay it to the government.
This means using accounting software to do financial tasks instead of doing them by hand. It makes calculations faster and more accurate.
It tracks the buying of goods or services, including the cost and quantity of each purchase.
P2P (Procure-to-Pay) is the process that starts when a business orders goods or services and ends when it pays for them. It includes everything from ordering to receiving the bill and making the payment.
Dividends are payments made to shareholders from a company’s profits. They are a way to share the earnings with the owners of the company.
Charitable institutions employ fund-based accounting to monitor funds allocated for particular objectives, guaranteeing their proper use.







