Table of Contents
- Understanding Inventory: Definition and Examples
- Key Takeaways on Inventory
- Types of Inventories
- Key Examples of Inventory in Different Businesses
- What Is Inventory Analysis and Why Is It Important?
- Benefits of Inventory Analysis
- The Importance of Inventory Control
- Inventory Best Practices
- Understanding Inventory Turnover and Turnover Ratio
- What Inventory Can Reveal About a Business
- How Vyapar App Can Help with Inventory Control and Management
- FAQ’s
What Is Inventory? A Simple Explanation
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes

Inventory, or stock, refers to the goods or materials a business keeps selling to customers or uses to make products. Good inventory management helps a business have enough stock to meet customer demand. It also prevents having too much stock, which can raise costs. Proper stock management is essential for smooth business operations, customer satisfaction, and financial health.
Understanding Inventory: Definition and Examples
In simple terms, stocks are the items a business owns to sell or use in making products. These items are essential for the business because they directly impact sales and profit. Here are a few examples:
- A clothing store’s inventory includes clothes like shirts, pants, and jackets that are ready for sale.
- A bakery stocks ingredients like flour, sugar, and butter, and it also offers baked goods that are ready for sale.
- A car dealership’s stocks include cars on the lot that are ready to sell to customers.
Every business has its own inventory needs. Managing these needs well keeps operations running smoothly and customers satisfied.
Key Takeaways on Inventory
- Inventory, or stock, is the goods a business holds to sell or use in production.
- It includes raw materials, items in progress, and finished goods ready to sell.
- Managing inventory well prevents shortages, reduces costs, and keeps customers satisfied.
- Inventory management affects a business’s operational efficiency, costs, and ability to meet demand.
Types of Inventories
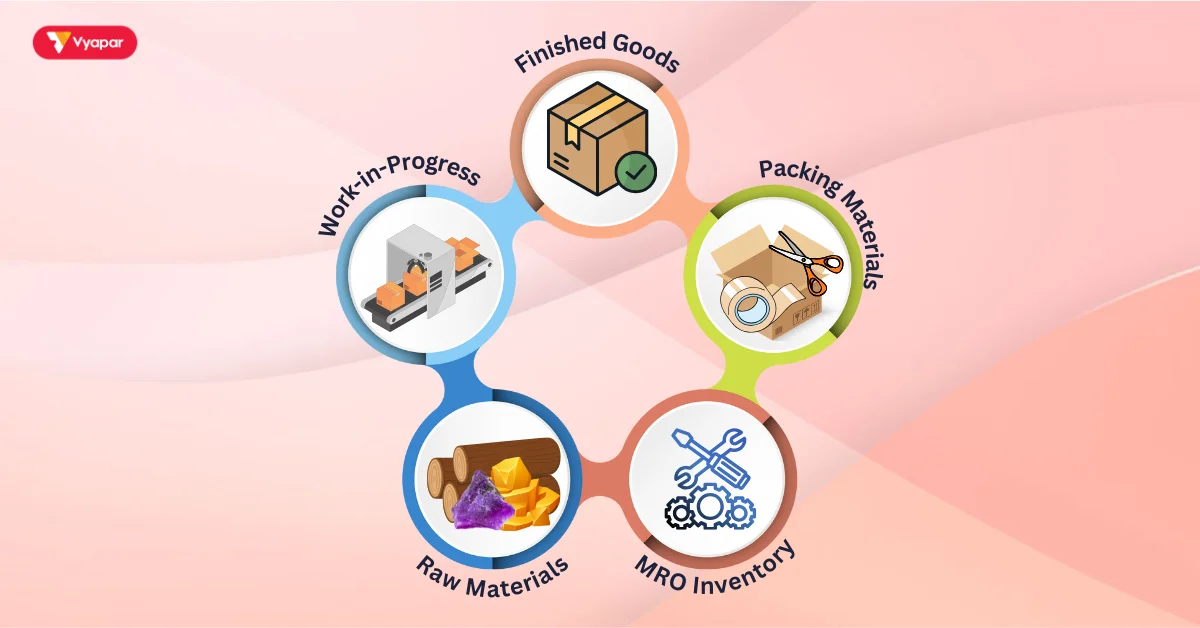
Several types of goods exist based on the stage they’re in for production or sale:
- Raw Materials: Basic materials used to make products. For example, wood is a raw material for furniture makers, and flour is a raw material for bakeries.
- Work-in-Progress (WIP): Products that are midway through the manufacturing process. For instance, people consider wood that someone has cut but not yet transformed into furniture as WIP inventory.
- Finished Goods: Products that someone has fully completed and made ready for sale. For an apparel shop, this would encompass products such as tops and trousers.
- Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) Inventory: These are supplies that keep the production equipment working well. They include tools, cleaning supplies, and replacement parts.
- Packing Materials: Items like boxes, tapes, and labels used to package goods before shipping or displaying them for sale.
Knowing the different types of stock helps businesses manage their stock better. This ensures they have the right amount of each type available.
Key Examples of Inventory in Different Businesses
Different industries have different inventory needs:
- Retail: Clothes, shoes, groceries, and electronics ready to sell.
- Manufacturing: Raw materials like metals, wood, or parts for assembling finished goods.
- Food and Beverage: Ingredients like flour, spices, and cooking oil are used in recipes.
- Agriculture: Harvested crops, animal feed, and fertilizers.
- Automobile: Automobiles, replacement components, and equipment for fixes.
Each type of business needs an inventory management strategy that suits its unique operations.
What Is Inventory Analysis and Why Is It Important?
Inventory involves examining stock levels, analyzing sales patterns, and assessing customer demand. This helps businesses know how much stock to keep, which items sell well, and which items are too much. Analyzing inventory correctly prevents shortages and excess stock. This helps a business run smoothly and efficiently.
Inventory assessment is important because it evaluates stock levels and trends.
- It reveals patterns in customer demand, helping businesses stock popular items.
- It identifies excess inventory that occupies space and increases carrying costs.
- It helps with planning, ensuring businesses have safety stock to avoid running out.
- It saves money by preventing over-ordering, which ties up cash in unsold goods.
Benefits of Inventory Analysis
- Reduced Carrying Costs: Keeping only the needed stock helps lower storage and warehousing expenses.
- Better Demand Forecasting: Knowing which items sell fast helps businesses predict what to stock in the future.
- Improved Cash Flow: By holding the right amount of stock, businesses free up cash for other needs.
- Higher Profit: Effective stock management prevents losses from unsold goods, improving profits.
The Importance of Inventory Control
Inventory control means managing stock levels carefully to avoid shortages or excesses. A good inventory control system helps businesses manage their stock. This reduces costs and makes sure items are available when customers need them.
Good stock control helps by:
- Maintaining Customer Satisfaction: Ensures that items are available when customers want them.
- Reducing Holding Costs: Minimizes costs by keeping only what’s necessary in stock.
- Minimizing Waste: Reduces the risk of goods expiring or becoming outdated.
Inventory Best Practices
Some best practices to keep stock organized and efficient include:
- Regularly Check Stock Levels: Keeping track of inventory on hand helps businesses avoid running out or overstocking.
- Use Inventory Management Systems: Software like Vyapar automates tracking and updates, reducing manual work and errors.
- ABC Analyzing: Split stock into three groups (A, B, and C) based on their value and importance. Focus on managing high-value items closely.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) System: Order stock only when you need it, which reduces carrying costs.
- Set Safety Stock Levels: Set minimum stock levels to ensure popular items are always available.
Understanding Inventory Turnover and Turnover Ratio
Inventory turnover measures how often a business sells and replaces its stock within a given time. A high turnover rate usually means items are selling fast. A low turnover rate may suggest overstocking or slow sales.
You calculate the inventory turnover ratio by dividing the cost of goods sold by the average inventory. For example, if a business has ₹100,000 in sales and ₹20,000 in average inventory, the turnover ratio is 5. This means someone sold the stock and replaced it five times during that period. Turnover ratio helps businesses see if their stock levels are efficient or if they need to adjust ordering habits.
What Inventory Can Reveal About a Business
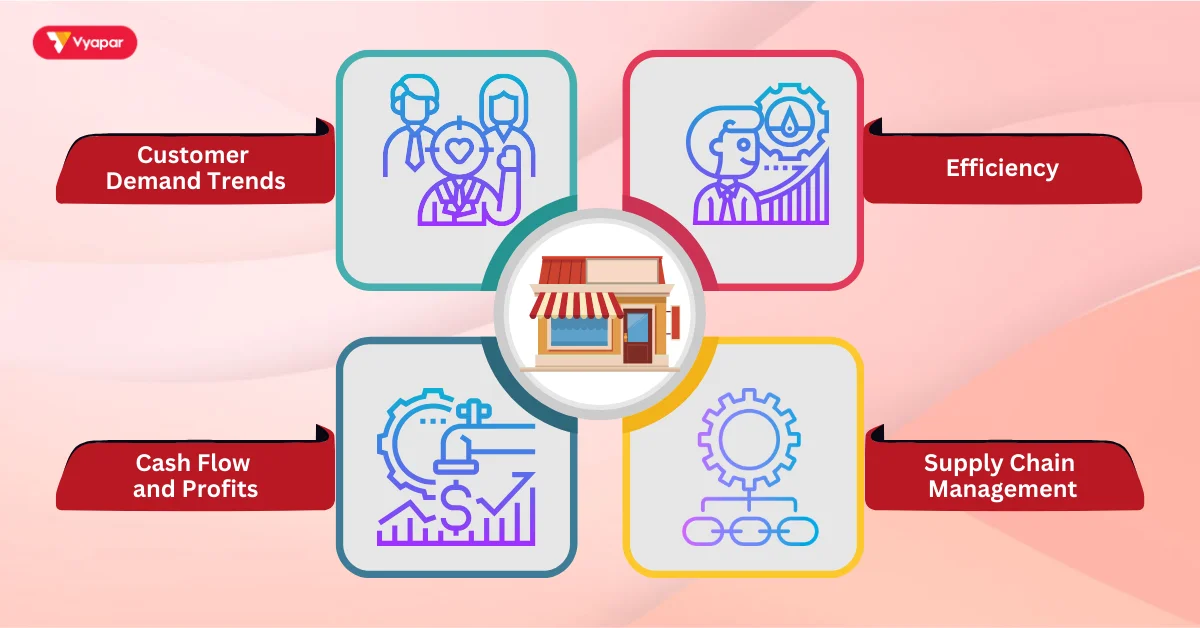
Goods reveal a lot about how a business operates:
- Customer Demand Trends: The amount of stock shows what customers buy most often.
- Efficiency: Well-organized stock shows good operational efficiency.
- Cash Flow and Profits: High levels of excess stock can tie up cash and affect profit margins.
- Supply Chain Management: Proper stock management reveals how smoothly the business’s supply chain is running.
How The Vyapar App Can Help with Inventory Control and Management
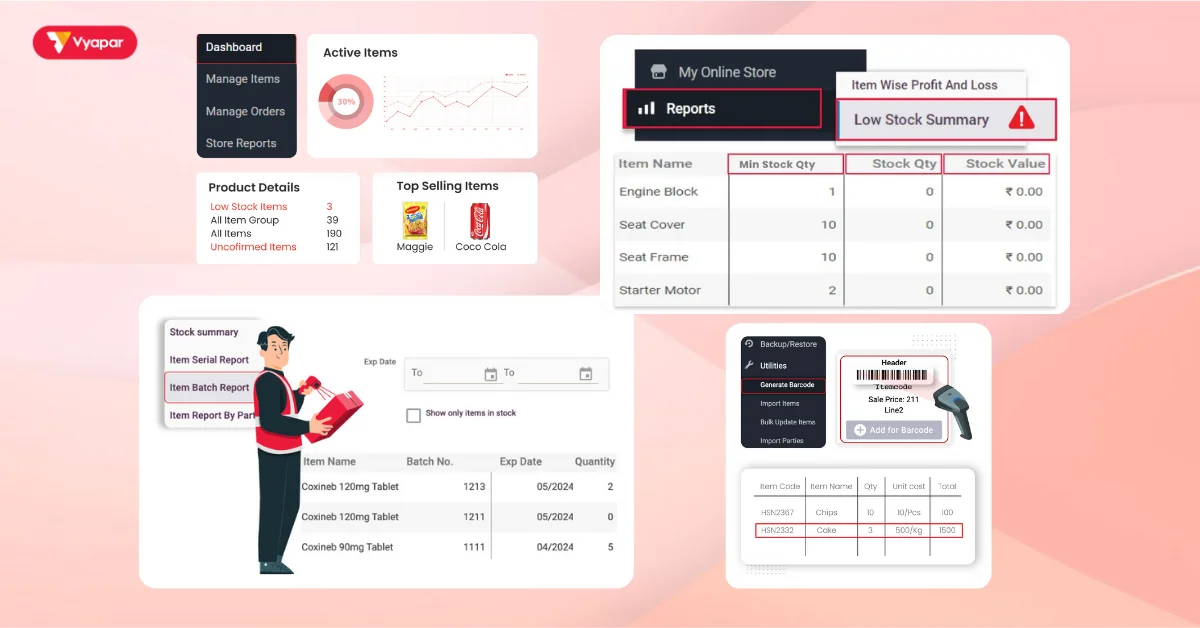
The Vyapar App is an inventory management software that helps small and medium-sized businesses manage their stock effectively. Here’s how Vyapar can make stock control easier:
- Real-Time Stock Tracking: Vyapar helps businesses check stock levels right away. In this manner, they are always aware of the stock and when to restock.
- Automatic Stock Alerts: The app sends alerts when stock reaches minimum levels, preventing shortages of popular items.
- Detailed Stock Reports: Vyapar generates reports on stock levels, turnover, and item costs, helping businesses make informed decisions.
- Batch and Expiry Tracking: For businesses with perishable items, Vyapar helps track batches and expiry dates. This prevents losses from expired goods.
- Set Custom Stock Levels: Businesses can set minimum and maximum levels for each product. This helps them keep the right amount of stock available.
- Barcode Integration: Vyapar supports barcode scanning, making it easy to track stock movements accurately.
- Stock Valuation: Vyapar helps with valuing stock, allowing businesses to monitor the cost and price of goods effectively.
- Supports Supply Chain Management: Vyapar helps businesses manage their supply chain better. It tracks stock levels and stock movement, keeping operations running smoothly.
Using Vyapar for stock management saves time and cuts costs. It helps businesses keep the right stock levels. This improves cash flow and keeps customers satisfied.
Are you a Business Owner?
Take your business to the next level with Vyapar! Try free!
Try our Android App (FREE for lifetime)
FAQ’s
Inventory, or stock, is the goods or materials a business holds to sell or use in production.
Stock helps businesses meet customer demand and keep operations running smoothly. Proper management prevents running out of goods or holding too much.
Common types include raw materials, work-in-progress, finished goods, MRO supplies, and packing materials.
Evaluating inventory means examining stock levels and trends to avoid overstocking or running out of popular items.
Inventory turnover measures how often businesses sell and replace stock in a given period. It indicates whether someone manages stock levels well.
Vyapar offers real-time tracking, stock alerts, reports, and barcode scanning, making inventory control simple and efficient.








