Depreciation Account Format
Download Depreciation Account Format to track your business requirements easily. Or use the Vyapar App to run your business without any technical knowledge in accounting!!. Avail 7 days Free Trial Now!


Download Free Depreciation Account Format
Highlights of Depreciation Account Format
We’ve put in a lot of effort to make sure you get the best template possible

All versions are print friendly

Built from scratch

Include essential invoice elements

Automatically calculate subtotal & grand total amount

Consistently formatted
What is the Depreciation Account?

Depreciation in accounting refers to when assets lose value over time until the asset’s value becomes zero or negligible. Depreciation can happen virtually with any fixed asset, including office equipment, Personal computers, machinery, buildings, etc. One thing that is exempted from the fixed asset is the value of land, which appreciates (increases) over time.
What is the Benefit of Using the Depreciation Account?

Offers the Matching Cost:
One significant preferred advantage of depreciation accounting of the asset is that it assists the organizations in reasonably expressing the measure of cost acquired because of utilizing a benefit during an accounting period to coordinate appropriately with the income the asset expects to create in a similar period.
Without properly charging an asset’s buy cost to depreciation accounting or depreciation cost, organizations may downplay or exaggerate total costs and, in this manner, misquote incomes, revealing misleading cash-related data to the buyer.
Helps in Expense Recovery:
Depreciation cost offers a route for recuperating the buy cost of an asset. Dissimilar to resource expensing, organizations can recoup an asset’s expense promptly. Utilizing resource depreciation, organizations recuperate all out resource costs over the valuable existence of the benefits through occasional depreciation cost of the particular asset.
Depreciation accounting is a non-money charge against income earned by an individual or an organization, enabling particular organizations to put aside part of the income as assets for future resource substitution. Without charges of depreciation cost, the bit of income may have been utilized for different purposes, which may not be used as it can be.
Company’s Asset Valuation:
Utilizing depreciation cost through depreciation accounting helps organizations report assets at their net book esteem. Organizations first record the value of the fixed assets at their unique buy costs.
In any case, asset worth decays after some time as the consequence of the advantage utilizing that possible reason for an advantage’s mileage. In this way, organizations must modify an asset’s value to its outstanding net worth.
An asset’s net book worth is the first buy cost subtracted by the aggregated benefits depreciation, the total depreciation of goods and commodities, and the cost from every past time.
How Many Types of Depreciation are There?

There are four types of depreciation which are given down below:
Straight-Line-Method:
The straight-line method is the most basic way to record the depreciation of assets. It reports an equal depreciation expense annually throughout the entire useful life of the asset until the entire asset is depreciated to its salvage value or the retrieved value.
Let us understand the straight-line method through an example of a company. Sun Pharma buys a machine at the cost of INR10,000. Sun Pharma decides on a salvage value of INR2,000 and a useful life of five years. Based on these assumptions of Sun Pharma, the depreciable amount is INR8,000 (10,000 cost – 2,000 salvage value).
The annual depreciation of assets by using the straight-line method is calculated by dividing the depreciable amount by the total number of years. In this case, it amounts to INR 1600 per year (8,000 / 5). It results in a depreciation rate of 20% (INR 1600 / INR 8,000).
Declining Balance:
The declining balance method is used as an accelerated depreciation method. This method depreciates the cost of the machine at its straight-line depreciation percentage times its remaining depreciable amount annually.
As an asset’s carrying value is higher in previous years, the same percentage causes a larger depreciation expense amount in previous years, which is declining with each year.
The formula for Declining Balance Depreciation = (Net Book Value – Salvage Value) x (1 / Useful Life) x Depreciation Rate
While using the straight-line example above, the machine costs INR10,000, has a salvage value of INR 2,000, a five-year life, and is depreciated at 20% each year, so the expense is INR 1600 in the first year (INR8,000 depreciable amount x 20%), INR 1280 in the second year ((INR8,000 – INR 1600) x 20%), and so on.
Double-Declining Balance (DDB):
The double-declining balance (DDB) method is another accelerated depreciation method. After taking the reciprocal of the asset’s useful life and doubling it as your preferred value.
This rate is applied to the depreciable base of its book value for the remainder of the asset’s assumed life. Thus, it is essentially two times faster than the declining balance method.
The formula for DDB = (Net Book Value – Salvage Value) x (2 / Useful Life ) x Depreciation Rate
Let us understand through an example here, suppose an asset with a useful life of five years would have a reciprocal value of 1/5 or 20%. Double the rate or 40%, is applied to the asset’s current book value for depreciation.
Although the rate remains constant, an asset’s rupee value will decrease over time because the rate is multiplied by a smaller depreciable base for a given period.
Sum-Of-The-Year’s Digits (SYD):
The sum-of-the-year’s digits (SYD) method allows for accelerated depreciation. Start by combining all the digits of the assumed life of the asset for a given period.
Let us understand the sum-of-the-years through an example of an asset with a five-year life that would have a base of the sum of the digits one through five, or 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = 15. In the first depreciation year, 5/15 of the depreciable base would be depreciated by the asset’s value.
In the second year, only 4/15 of the depreciable base would be depreciated by the asset’s value. It will continue until year five depreciates the remaining 1/15 of the base.
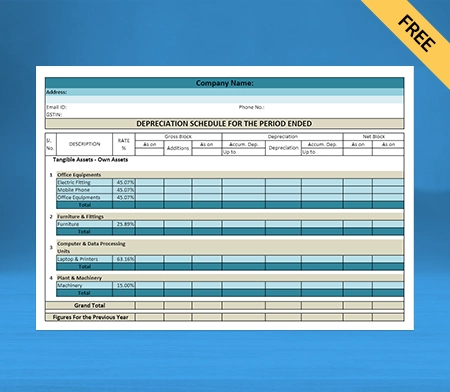
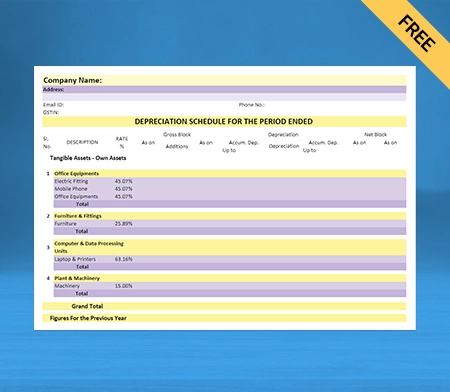
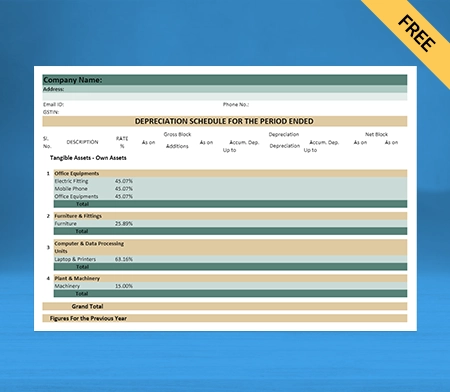
What does the Depreciation Schedule Mean?

A depreciation schedule is referred to a table that shows you how much each of your assets will be depreciated over the years. It typically contains the following information given down below:
- It has the description of the asset and the date of purchase
- It accommodates the total price you paid for the asset and the expected useful life
- The Depreciation method used the Salvage value as how much you can sell it for once as it has a useful life, for example, how much a scrapyard would pay for your old work truck.
- The depreciation amount, which is deductible in the current year and the cumulative depreciation amount
- The resulting net book value of the asset is referred to as the total price paid minus any cumulative depreciation.
How are the Assets Depreciated for Tax Purposes?

People often talk about depreciation when they refer to accounting depreciation of assets. It allocates an asset’s cost throughout its useful life to align its expenses with revenue generation for the retailer and organizations.
Businesses also generate accounting depreciation schedules with tax benefits in mind because depreciation on assets over time is deductible as a business expense following Government of India rules.
Depreciation schedules can range from simple straight-line to accelerated or per-unit measures per rule.
Accumulated Depreciation vs Depreciation Expense

A depreciation schedule is referred to a table that shows you how much each of your assets will be depreciated over the years. It typically contains the following information given down below:
- Accumulated depreciation refers to the total depreciation incurred on an asset. Meanwhile, depreciation expense is the amount of the cost of an asset allocated and reported at the end of each reporting period as per the government rules.
- While accumulated depreciation is reported on the balance sheet, on the other hand, depreciation expense is reported in the income statement.
- Accumulated depreciation results in a credit to the organization. Meanwhile, the balance in depreciation expense results in a debit.
- Accumulated depreciation is deducted from the original cost of an asset related to retail or organization. Meanwhile, depreciation expense is calculated by subtracting the value of an asset of particular things that are likely to be retained when totally depleted from the asset’s value at the time of acquisition and then dividing the result by the asset life span.
Why is the Depreciation Accounting Format Essential for Small Business?

So now we know the meaning of depreciation. These methods are used to calculate depreciation accounting format and inputs required to calculate them, and we also saw examples of how to calculate depreciation accounting format.
Let’s find out why small and medium size businesses should care to record depreciation.
As we already know, the depreciation accounting format’s purpose is to match the cost of the fixed asset over its productive life to the revenues the business earns from the asset. It is very hard to link the asset’s cost to revenues directly.
Hence, the cost is usually assigned over the years. The asset is productive and can be used in the future. Over the fixed asset’s useful life, the cost is moved from the balance sheet to the income statement earned by small retail businesses.
Alternatively, it is just an allocation process per the matching principle instead of a technique that determines the fair market value of the fixed asset over the years. If we do not use depreciation accounting, we have to charge all assets to expense once bought, which is detrimental to companies’ business.
It will result in huge losses in the following transaction period and high profitability in periods when the corresponding revenue is considered without an offsetting expense. Companies that do not use depreciation expenses in their accounts will incur front-loaded expenses and highly variable financial results.
Benefits of Using the Vyapar App
Business/Accounting Management:
You can manage the single store and the chain of stores using the Vyapar Depreciation Account maker app. You can use it for registered and unregistered businesses as per your own need and requirement here.
By using the Vyapar, you can easily have data access on single and multiple devices simultaneously. You can also create GST and non-GST transactions that comply with the government of India rules.
You can also create multiple companies and up to five firms within a firm by using the Vyapar billing software. Vyapar Depreciation Account formats make every possible effort to make your business procedure smoother and quicker and gear you with every tool required for your small business’s success.
It also allows you to know your income statement. You can also use the depreciation accounting format as per your requirement as it comes in three formats PDF, Word, and MS Excel in Vyapar.
Instant Inventory Status Checks:
Using the Vyapar Depreciation Account generator app, you can know your exact inventory and receive on-time notifications on your smartphones and personal computers when some stocks are low. You can simplify purchasing by knowing the cost of fixed goods as in your online catalogue service of Vyapar, digitally tracking all orders and inventory on a single platform.
So you can keep your balance sheet clear and profitable. You can also customise the depreciation accounting format as per your requirements. By using the auto stock management of Vyapar, you can check the stock quantity, reserved quantity, and stock value both automatically and manually.
Using the extensive inventories, users may directly import items through Word or Excel sheets and can add the stock information based on the given format. You can also use Vyapar’s powerful stock control system, gain visibility over your operation process most of the time, and check the unit of production method.
Offline/Online Software:
Vyapar Depreciation Account formats allow you to manage Depreciation Accounts and manage your business operation online and offline. Either you are doing your business from remote areas across the country, especially in the hilly and mountainous regions or densely forested areas where you frequently face the problem of poor network and internet connection.
You can simultaneously operate the depreciation accounting format online and offline, so you can easily calculate depreciation and depreciation methods.
Tourism guides and Business owners must frequently travel across and outside the country. Here, Vyapar billing software operates in both online and offline modes simultaneously. And helps you to calculate the amount of depreciation through the depreciation accounting format.
Online-Store:
With the help of Vyapar billing software, you can set up your online catalogue store. You can list all of the products or services you sell to your customers, and it will assist you in presenting a catalogue of all the services/products to customers.
It will help you amplify your online sales seamlessly and widen the area of your reach simultaneously. So your goods and products can reach a large number of people simultaneously.
The best part of using Vyapar’s billing software online store features is you don’t have to pay a dime from your pocket for using additional features. These features help you take your business online and can increase the range of your small business product to a range of people. India.
You can directly send the link to your online store to your customers so they can easily reach your catalogue platform without difficulty. Your computers can pick products and place orders online from your store. You can easily customise the depreciation accounting format per your requirement in all three formats, PDF, Word and MS Excel, available on the Vyapar app.
Multiple Modes of Payment:
Vyapar Depreciation Account Maker app comes with multiple modes of payment, both online and offline. You can use online substitutes such as debit/ Credit cards, Online net banking, IMPS/RTGS/ E-Wallet, etc. You can also use the Quick Response code and UPI to send and receive payments from your clients seamlessly.
You can also check the income statement by using the Vyapar billing software. Vyapar depreciation account formats ensure every possible way to make your business work smoother and quicker. You can also use offline substitutes such as cash and cheque with your clients.
Using multiple payments helps avoid friction with your clients over the payment method. Compared to other apps Vyapar can simultaneously make your business more professional and lucrative for your customers. You can also check the depreciation rate through the straight-line method in Vyapar.
Are you a Business Owner?
Take your business to the next level with Vyapar!
Try our Android App (FREE for lifetime)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs’)
You can access the depreciation accounting format in all three available formats PDF, Word, and Excel. Using the Vyapar app, you can access all three formats. You don’t need to worry about searching these given formats separately.
Tracking the depreciation expense of an asset is essential for reporting purposes because it spreads the cost of the asset over the years it has been in use. The simplest way to calculate this expense’s depreciation rate is to use the straight-line method.
The formula for straight-line methods is (cost of asset minus salvage value) divided by useful life. You can customise the depreciation accounting format in all three formats per your requirement.
In accounting, a depreciation account is referred to as the debit balance since it is an expense. And an offset to this is a credit balance for an accumulated depreciation over the period asset being in use, which is a contra entry.
Depreciation is a type of expense that reduces the carrying value of an asset over the pere it is in use. It is an estimated expense that is scheduled rather than an explicit expense, and the depreciation is generally found on the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
Depreciation is recorded on the income statement as the expense and represents how much of an asset’s value has been used for that particular year. As a result, it is not referred to as an asset or a liability.
To calculate the depreciation Value of the asset using the straight-line method, subtract the asset’s salvage value (what you expect it to be worth at the end of its useful life) from its cost.
The final result is the depreciable basis or the amount that can be depreciated over time. Divide this amount by the numbers the asset is in use.
Depreciation is an expense used to reduce an asset’s carrying value over time. It is an estimated expense scheduled for the future rather than an explicit expense. You can find the Depreciation value on the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.





