What is Manufacturing? A Complete Guide to Manufacturers
Estimated reading time: 11 minutes

Manufacturing is the process of turning raw materials into finished products. You use tools, labor, machinery, and technology to produce items that you can use or sell. Almost everything we use daily comes from production processes, whether we consider food, electronics, clothes, or vehicles.
For small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) in India, knowing how these production methods work can help improve operations. This understanding can also lower costs and enhance product quality. In simple terms, manufacturing takes ideas and raw materials and turns them into tangible products.
Definition and Explanation
At its core, manufacturing is the transformation of raw materials into a finished product. The production process can change a lot. It depends on the type of product, the scale of production, and the level of customization needed. Whether you are making one product or thousands, knowing about different manufacturing processes is key to success.
For example, a t-shirt company might use batch processing to make hundreds of t-shirts at the same time. In contrast, a small custom workshop may use job shop manufacturing to create unique items made for each customer.
Major corporations employ the assembly line method. It entails workers or machinery repeatedly performing specific tasks. This technique is excellent for producing large volumes of goods.
Key Takeaways on Financial Statements
✅ Manufacturing transforms raw materials into finished products.
✅ Different production processes include mass production, batch manufacturing, and custom fabrication.
✅ The type of manufacturing method you choose depends on your product, volume, and custom option needs.
✅ Quality control is essential to ensure consistency and safety in the final product.
✅ Lean manufacturing helps improve efficiency by reducing waste.
Types of Manufacturing Processes
Different types of production methods exist. Choosing the right one is important for businesses. This helps them meet customer demands efficiently. Here are the most common methods used in the industry:
1. Mass Production

Mass production is common in industries that produce a high volume of identical products. A highly cost-effective way exists for companies that produce large quantities of the same product.
Machines and assembly lines help automate repetitive tasks. A prime example is the automobile industry, where workers assemble vehicles in a step-by-step manner. Mass production is efficient, but it may limit custom options.
Car manufacturers produce hundreds of identical vehicles on an assembly line.
2. Batch Process Manufacturing

In contrast, batch manufacturing involves producing products in smaller batches. People often use it when they need multiple variations of a product. For instance, a bakery might bake different types of bread in separate batches throughout the day.
Batch manufacturing is often more flexible than mass production. However, it may not be as cost-effective for high-volume needs.
A bakery produces batches of different bread types each day.
3. Continuous Process Manufacturing

Industries like petrochemicals or chemicals continuously process raw materials. This process is ideal for companies that deal with products requiring constant production flow over long periods. The oil refinery is a good example of continuous process manufacturing. In this process, refineries turn crude oil into gasoline, diesel, and other fuels.
Oil refineries work 24/7 to refine crude oil into usable products like gasoline and diesel.
4. Job Shop Manufacturing

This method is most beneficial for companies creating small, custom orders, often with low production volumes. A metalworking shop might produce parts for various clients, customizing each product based on specific customer needs. This method offers flexibility but is less efficient than mass production for large quantities.
A custom metal workshop producing parts on demand for customers.
5. Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing focuses on improving efficiency by reducing waste. This involves streamlining production processes to eliminate unnecessary steps, reduce inventory, and improve productivity. The goal is to produce high-quality products with minimal resources.
In a small toy factory, lean manufacturing cuts waste. It does this by using less raw material. This may lead to save employee time. Lean manufacturing makes production easier and faster.
6. 3D Printing
3D printing is a modern way to make things. It creates objects layer by layer using materials like plastic or metal. Especially useful for creating prototypes or small batches of custom products.
The 3D printing process helps businesses make detailed items. These items would be hard or costly to create with traditional methods.
A custom jewelry designer might use 3D printing to create a unique piece of jewelry for a client.
Stock MTS (Make to Stock) vs Order MTO (Make to Order)
When managing production lines, there are two major approaches businesses use for creating products:
- Stock MTS (Make to Stock): Products are made in advance and stored in inventory. People usually use this for products that have steady demand. The company can predict customer needs and make goods in advance.
A toy maker might create many dolls and keep them in warehouses. They are ready to ship when customers order.
- Order MTO (Make to Order): In this case, products are only made when a customer places an order. Ideal for businesses offering custom or highly specialized products.
A custom furniture business starts making a sofa only when a customer tells them the design and size they want.
Quality Control
Quality control is the process of ensuring that the products meet certain standards. It involves checking each item to ensure it works correctly, is safe to use, and is free from defects. For businesses, having an effective quality control process is crucial for customer satisfaction and maintaining a good reputation. A shoe company will have quality checks. These checks ensure that each pair has no defects. They also check that the stitching is correct, and the materials are strong.
Final Product
Once a product completes the manufacturing process, it becomes ready for sale or use. The final product is the completed item. The team gets it ready for delivery or distribution after finishing all production steps.
Smartphone manufacturing involves multiple steps to ensure a complete product. First, someone sets up the display, and then they insert the battery. Following this, an individual installs the necessary software onto the device. Ultimately, the team prepares the phone for shipment to retail stores, making it available for customer purchase.
Benefits of Manufacturing for MSMEs
Small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) can gain many benefits from getting involved in production. These benefits can help them succeed.
- Improved Cost Efficiency: By making the production process better, businesses can lower costs. Using methods like lean manufacturing helps reduce waste.
- Increased Profits: When production is efficient, businesses can better meet customer demand. This could result in increased sales and elevated profit margins.
- Customization and Flexibility: Methods like job shop manufacturing allow businesses to create personalized products, which can attract more customers.
- Job Creation: The manufacturing process creates employment opportunities, benefiting local communities and contributing to the economy.
- Consistent Product Quality: Quality control makes sure each product meets safety and performance standards. This helps businesses build trust with their customers.
How Vyapar Helps with Manufacturing
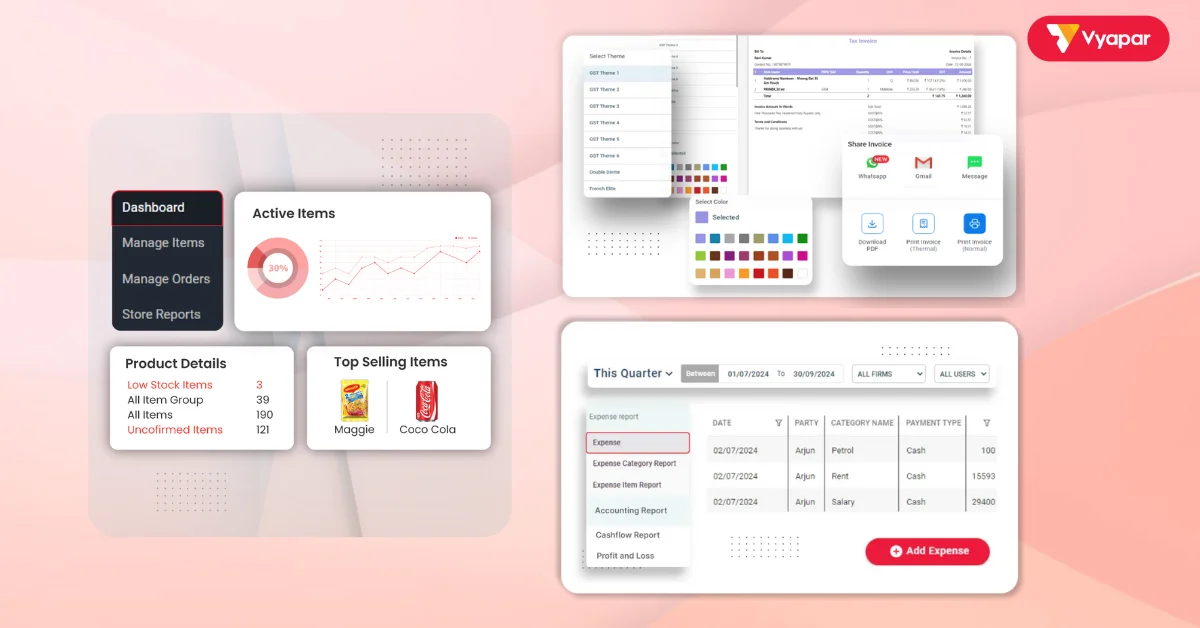
Vyapar is a business management software that simplifies many aspects of running a manufacturing business. It helps SMEs streamline their operations by automating tasks like inventory management, invoicing, and expense tracking. Here’s how Vyapar can help you:
- Inventory Management: Vyapar allows you to track raw materials, finished products, and stock levels in real-time. This helps you avoid shortages or excess inventory, which can lead to financial losses.
- Invoice Generation: You can easily generate GST-compliant invoices and manage your billing process. This ensures that your business stays organized and avoids potential tax-related issues.
- Expense Tracking: Vyapar lets you track expenses related to production, including raw materials, labour, and overhead costs. This helps you understand your profitability better.
- Order Management: You can keep track of customer orders and shipments, making it easier to fulfil orders promptly.
Are you a Business Owner?
Take your business to the next level with Vyapar! Use free trail!
Try our Android App (FREE for lifetime)
FAQ’s
Stock MTS means that manufacturers produce products ahead of time and keep them in storage. MTO orders mean that manufacturers make products only after customers place an order.
Lean manufacturing is a method that reduces waste in the production process to improve efficiency and save costs.
Quality control ensures that the final products meet certain standards of quality, including safety, functionality, and durability.
Production lines are systems where products go through different stages of making. Each worker or machine does a specific task.
3D printing makes complex products or prototypes by layering materials. This method is great for small batches or custom items.
Related Posts:









