Table of Contents
- What is a Financial Statement? A Guide to Everyone
- What Are Financial Statements?
- Key Takeaways on Financial Statements
- Why Financial Statements Are Important?
- Types of Financial Statements
- Uses of Financial Statements
- Benefits of Financial Statements for SMEs
- Common Challenges and Solutions in Managing Financial Statements
- How Vyapar Helps with Financial Statements
- FAQ’s
What is a Financial Statement? A Guide to Everyone
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes

Financial statements are essential documents that explain a business’s financial condition in simple terms. These statements summarize key financial information like revenue, expenses, profits, and cash flow over a specific time. They are a must for small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) in India as they help owners understand how their business is doing. You also need financial statements for important tasks like applying for loans, filing taxes, and planning for the future.
What Are Financial Statements?
A financial statement is like a business report card. It displays a business’s assets and liabilities and illustrates its profit.
These statements help businesses keep track of their financial condition. They provide insights into net income, operating expenses, and the overall financial health of the business.
For example, a shopkeeper can use financial statements to know if the shop is earning more money than it spends. This simple understanding can help in deciding how to spend money or save for the future.
Key Takeaways on Financial Statements
Give a quick overview of financial health and how the operations are performing.
Assistance with planning, budgeting, and making decisions.
Required for tax filing and securing business loans.
Why Financial Statements Are Important?
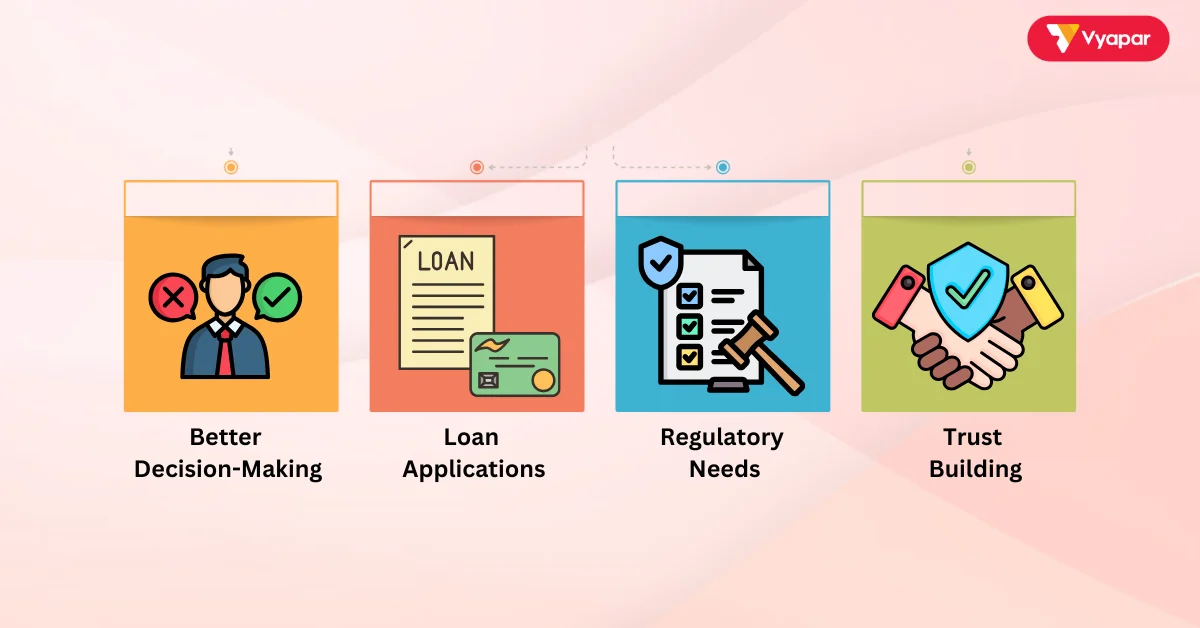
- Better Decision-Making: They help businesses understand revenue and expenses so owners can plan better. For instance, if expenses become too high, we can make adjustments to save money.
- Loan Applications: Banks usually request financial statements, such as the balance sheet or income statement. They do this to assess a business’s health before approving a loan.
- Regulatory Needs: Filing taxes like GST becomes easier when businesses maintain proper records through financial statements.
- Trust Building: When businesses share clear financial details, it builds trust with customers, partners, and investors.
Types of Financial Statements
Three main types of financial statements exist that businesses use to track their financial information:
1. Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position)

A balance sheet shows a business’s financial position at a particular moment. It lists all the assets, liabilities, and equity of the business.
Assets
Assets represent everything the business owns that has value. They can be categorized into different types:
- Liquid assets: refer to assets that people can quickly turn into cash. Examples include cash, accounts receivable, and marketable securities. Liquid assets provide a business with the flexibility to meet short-term financial obligations.
- Inventory: Inventory refers to the goods or raw materials a business keeps in stock for sale or production. It includes everything from finished goods ready for sale to raw materials that need processing.
- Long-Term Assets (Properties): These are physical items that a business owns for long-term use. Examples include buildings, machinery, and land. These assets are crucial for a business’s operations and typically depreciate over time.
Liabilities
Liabilities represent what the business owes to others. You must settle obligations through the payment of money or services in the future.
- Short-term liabilities include loans, accounts payable, and bills that businesses need to pay within a year.
- Long-Term Liabilities: These are debts or obligations that last more than one year. Examples include long-term loans, bonds, and lease obligations.
Managing liabilities is important. If a business fails to meet these obligations, It can lead to financial problems. This may also damage the business’s credit score.
Equity
Equity shows how much the owner has invested in the business. It reflects the value remaining after subtracting liabilities from assets. It represents the residual interest in the assets of the business after settling all liabilities. Equity can come from:
- Owner’s Initial Investment: The money or property that a business owner invests when starting or expanding the business.
- Retained Earnings: The business reinvests profits instead of giving them out as dividends to owners or shareholders.
A furniture store owner looks at the balance sheet. This enables them to determine if the store possesses sufficient cash or merchandise. This is necessary for settling short-term liabilities.
2. Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement)

This statement shows how much revenue a business has earned and what expenses it has paid during a period. It helps calculate the net income of the business.
Revenue
Revenue is the total income generated from the sale of goods or services before any expenses are deducted. People often call it “sales” or “sales revenue.” This is the primary source of income for any business and a critical indicator of its market performance.
- Gross Revenue: This refers to the total sales before any deductions, such as discounts, returns, or allowances.
Expenses
Expenses are the costs incurred in the operation of the business. These costs can vary depending on the industry and the nature of the business but generally include:
- Fixed Expenses: Costs that remain the same regardless of how much the business produces or sells, such as rent or salaries.
- Variable Expenses: Costs that fluctuate depending on the business’s activity, like raw materials or utilities.
Expense management is crucial as it directly impacts the business’s profitability.
Net Income
Net income, or profit, shows the money that remains after businesses deduct all expenses from revenue. A key indicator of a business’s profitability and overall financial health exists. A positive net income means the business is making a profit, while a negative net income indicates a loss.
Example: A bakery uses this statement to see which month had higher sales and which ingredients cost the most.
3. Cash Flow Statement

This tracks the money that comes in and goes out of a business. It helps us see if the business has enough cash for daily operations.
Operating Cash Flow
This is the money a company makes from its main activities, like selling goods and services. Positive operating cash flow shows that a business makes enough cash from its work. This cash covers costs and helps invest in growth.
Investing Cash Flow
This refers to cash used or gained from buying or selling long-term assets. These assets include property, equipment, or investments. For example, if the business buys a new machine, it would have a negative investing cash flow.
Financing Cash Flow
This is the cash flow that comes from borrowing or repaying money. It includes loans and contributions from shareholders. This can include new investments from owners or the repayment of loans.
Example: A small factory uses this to ensure they have enough cash to buy raw materials without delays.
Uses of Financial Statements
- Clear and Organized: The sections display financial information, including assets, liabilities, equity, and expenses. This makes it easy to understand.
- Accurate tracking summarizes revenue, cost of goods sold (COGS), and operating expenses neatly.
- Regulatory Compliance: These statements are necessary for meeting government rules, including GST filing.
- Automation Ready: With tools like Vyapar, businesses can generate these reports quickly without errors.
Benefits of Financial Statements for SMEs
- Regulatory Compliance: Simplifies GST filing, ensures compliance, prevents penalties, and maintains good standing with authorities.
- Access to Finance: Provides detailed records for lenders and investors, strengthening trust and enhancing funding opportunities.
- Improved Decision-Making: Highlights profitable products and services, aiding in budgeting and growth planning.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Identifies cost-reduction areas and process improvements, such as managing inventory turnover.
- Transparency and Accountability: Keeps stakeholders informed on financial health, building trust with employees, customers, and investors
Common Challenges and Solutions in Managing Financial Statements
Common Challenges
- Complexity: Many SMEs lack the expertise to prepare accurate financial reports, leading to time-consuming and error-prone processes.
- Inconsistent Data: Bad record-keeping can lead to financial statements that are incomplete or not trustworthy.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Changes in tax laws and accounting rules can confuse. This can raise the risk of not following the rules.
Solutions for Overcoming Challenges
- Automation Tools: Using software like Vyapar automates calculations, ensuring accuracy and compliance with the latest regulations.
- Regular Record Maintenance: Maintain daily transaction logs to keep financial data up to date and reduce errors.
- Professional Support: Periodic consultations with accountants or auditors help ensure accurate reporting and adherence to regulatory requirements.
By addressing these challenges proactively, SMEs can ensure their financial statements remain accurate, insightful, and beneficial for decision-making.
How Vyapar Helps with Financial Statements
Vyapar is a robust solution that simplifies the preparation and management of financial statements, making it ideal for SMEs. Here’s how it helps:
- Automated Report Generation: Instantly creates balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow reports, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors.
- Integration with GST Compliance: Automates GST calculations, generates tax-compliant invoices, and prepares accurate tax summaries to ease compliance requirements.
- Customizable Templates: Allows businesses to tailor financial reports with specific metrics, offering deeper insights into financial performance.
- Real-Time Updates: It automatically syncs data from transactions, inventory, and invoices. This keeps financial records always up to date.
- User-Friendly Interface: Designed for easy use by non-accountants, enabling business owners to generate professional financial statements effortlessly.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces reliance on expensive accountants for routine financial tasks, saving money for the business.
Vyapar empowers SMEs to streamline financial management, save time, and make informed decisions that drive growth.
Are you a Business Owner?
Take your business to the next level with Vyapar! Use free trail!
Try our Android App (FREE for lifetime)
FAQ’s
They provide insights into the financial health, profitability, and liquidity of a business.
Yes, software like Vyapar automates the process, making it simple for non-experts.
While not mandatory for unregistered SMEs, they are essential for growth, compliance, and financing.
Ideally monthly or quarterly, but at least annually for tax and audit purposes.
Vyapar automates calculations, ensures compliance, and eliminates manual errors.
Related Posts:









